中级微观经济学
参考:中英文课本
Note: 个人整理,并非知识点的完全复制,只供个人记忆;由于笔者就读于英文班,故部分术语使用英文方便理解;必然有很多拼写错误,请宽恕喵。
market
- demand curve, supply curve: x-price
alloconstraint
- budget set
- good1's opportunity cost
- 两个商品价格上升相同倍数相当于收入减少对应倍数
- refer to numeraire price
- multiply all price/income with a positive number, choice of the consumer can't change
taxes / subsidies / rationing
- quantity tax/subsidy--higher/lower price
- value tax/subsidy--
- rationing(配给)--预算集被砍掉一块
preferences
- strictly preferred:
- indifferent:
- weakly prefers:
- + =
- + ! =
axioms of consumer prefence
- Complete: 要么 ,要么 ,要么
- Reflexive: 任何消费束至少跟自己一样好
- Transitive: 传递性,懒得写了( )
- 要是能做出最佳选择,偏好必须服从传递性公理
Example
- perfect substitutes: 斜率为负的直线
- perfect complements:
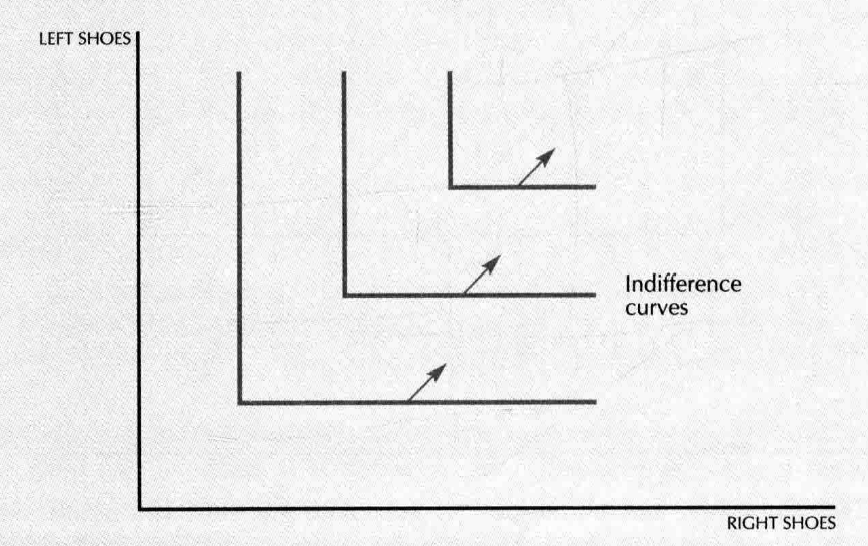
- bads
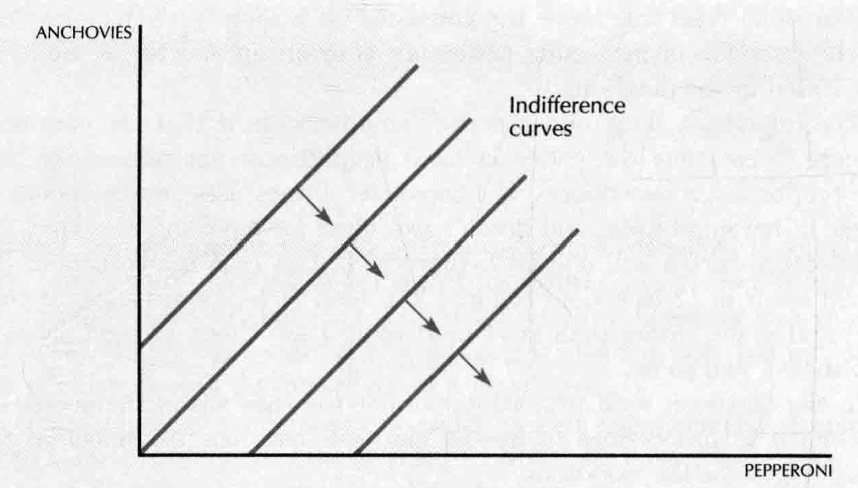
- neutral good
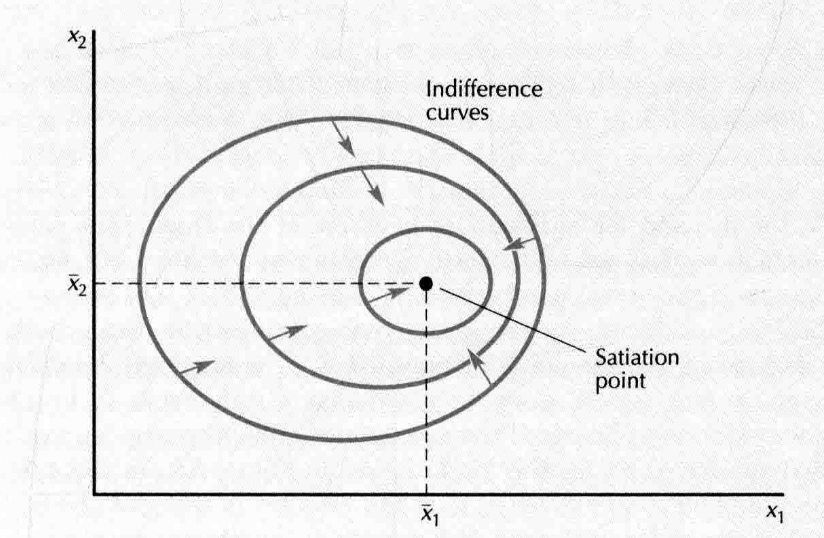
- Satiation
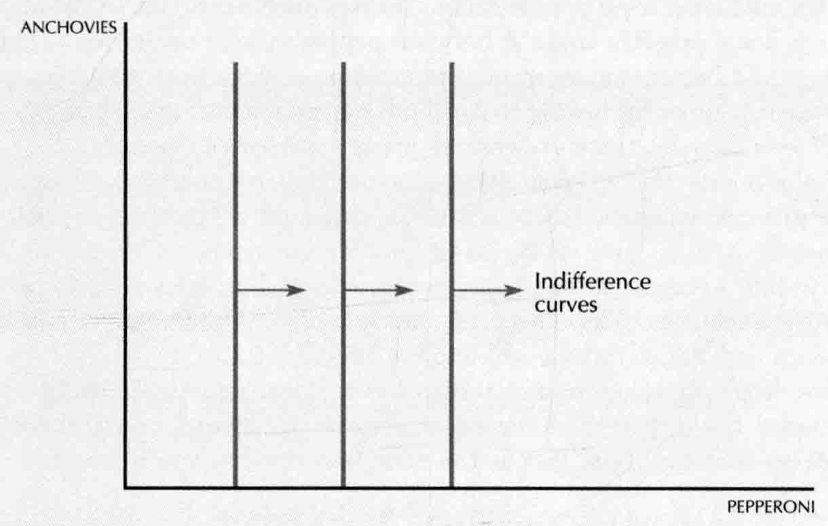
- discrete goods
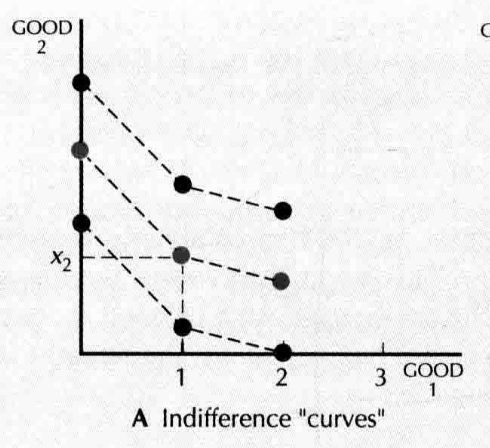
etc about preference
- well-behaved preferences:
- 满足:complete, reflective, transistive, 弱单调性,凸性
- 无差异曲线要是负的
- 消费束是凸集(convex preference)
- strict convexity: 无偏好曲线没有平坦的部分
- MRS: 无差异曲线的斜率。
- 交换率不等于边际替代率时,消费者总想用一种商品去交换另一种商品
- 若 则 MRS 为人们为了得到商品1的一个边际量而愿意放弃的货币数
- 人们为了得到商品1的一个边际量的额外消费而愿意支付的商品2的数量
Utility
- utility function--ordinal utility
- positive monotonic transformation of a utility function is a utility function that represents the same preferences as the original utility function
- perfect substtitutes:
- perfect complements:
- quasilinear prefenences: (效用对 是线性的,对 不是)
- Cobb-Douglas prefenences: standard example of indifference curves
- 是偏导
Choice
- optimal choice: boundary optimum/interior optimum
- for convex preference point that satisfies the tangency condition must be an optimal point
- interior potimum:
- perfect substitutes

- perfect complements(),
- neutrals and bads:
- discrete goods: 比较每个消费束的效用
- concave preferences: 最优选择是边界选择
- cobb-douglas preferences: 最优选择 ,
- 征收相同数量的税收的条件下,income tax is definitely superior to the quantity tax(对一个消费者,消费者的收入不会变化,忽略了供给对课税的反应)
Demand
- normal good:
- inferior good: (极端贫困的人收入增多可能会消费更多的低档商品)
- luxury good: demand for good goes up by a greater proportion than income
- necessary good: demand for good goes up by a lesser proportion than income
- ordinary good: demand for a good increase when its price decreases
- giffen good: demand for a good decrease when its price decreases
- giffen good must be inferior good, while inferior good may not be giffen good
- (gross)substitude:
- (gross)complement:
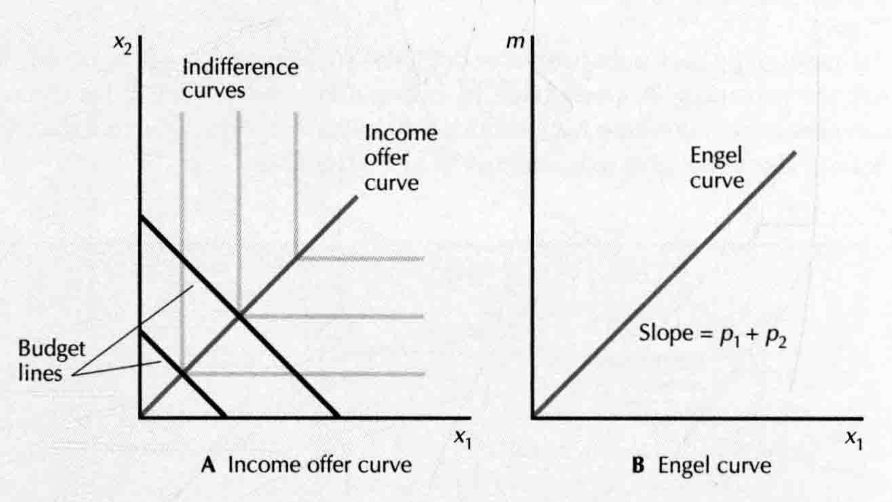
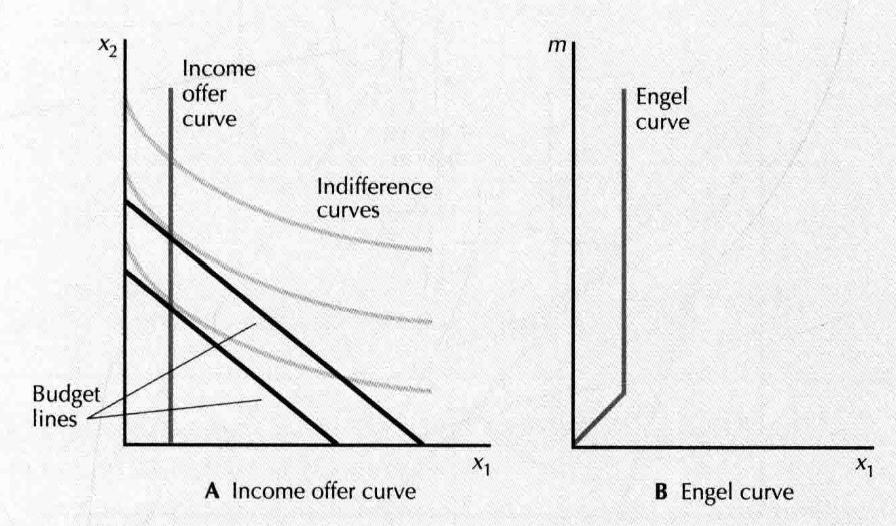
- income offer curve: 收入变化时,连接一系列的需求束,
- engel curve: (收入变化)
- demand curve: (价格变化)
- perfect substitutes:
- income change
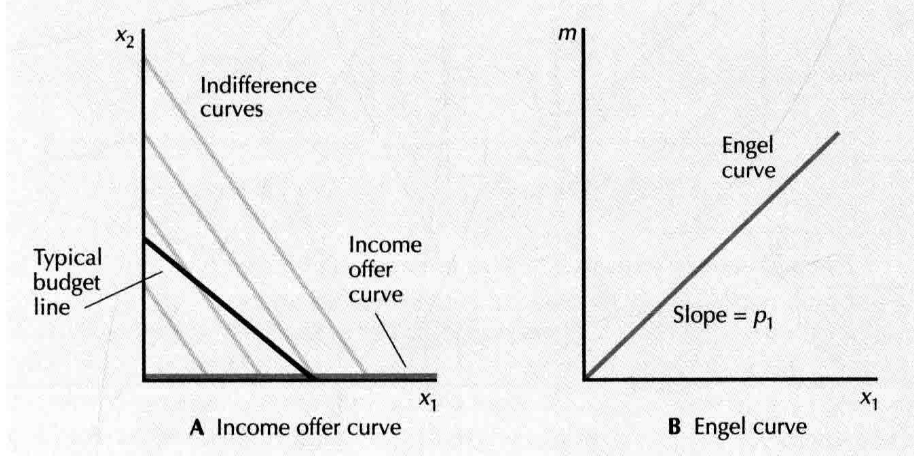
- price change
- income change
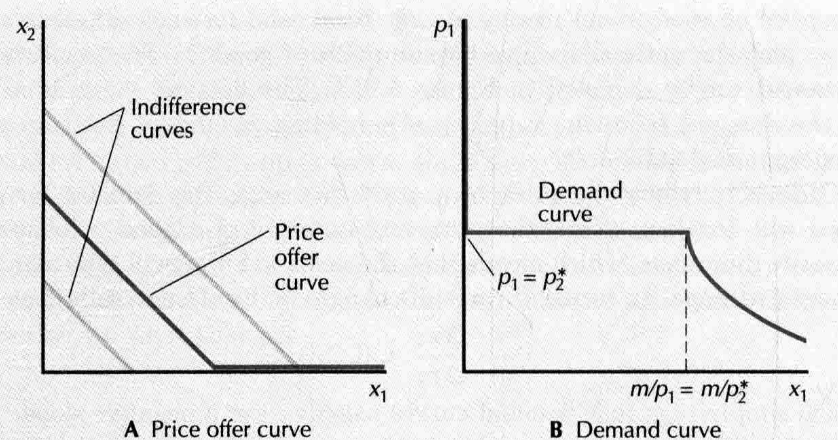
- perfect complements:
- income change
- price change
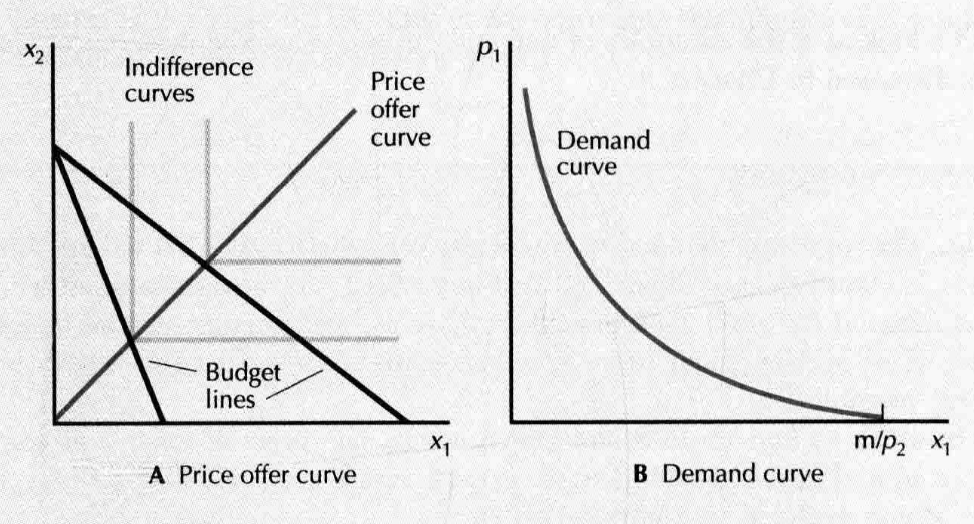
- income change
- cobb-douglas preferences:
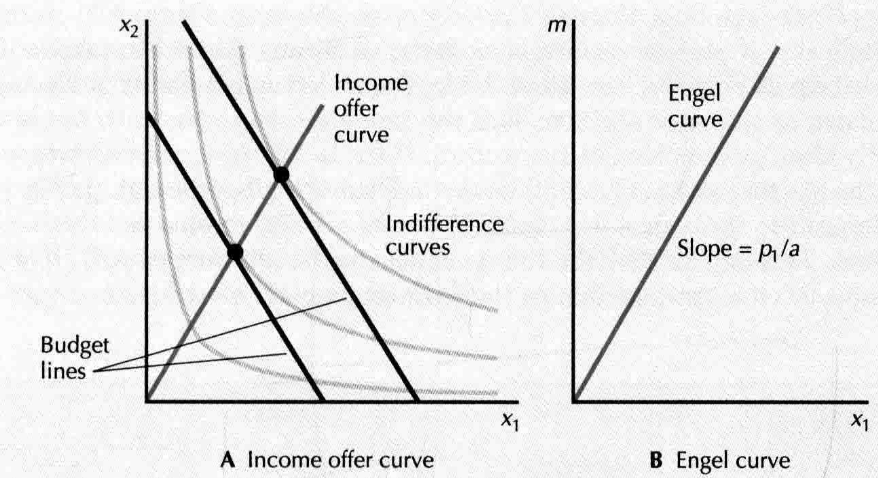
- homothetic preferences: if consumer prefers to , for any positive value of t, the consumer prefer to
- perfect substitutes, perfect complements, cobb-douglas are all homothetic preferences
- quasilinear preferences:
- demand curve: fixed and (is inverse or not depends on different point of view, 取决于谁是自变量)
- inverse demand function measures how many dollars the consumer is willing to give up for a little more good 1
revealed preference
- 显示偏好:如果在某一价格下面,消费者选择 而不是 购买,那么 显示偏好于 --- 若消费者总能在他能购买的消费束中选择他最偏好的,那么有
- directly/indirectly revealed preferred
- Weak Axiom of Revealed Preference(WARP): 直接显示偏好
- Strong Axiom of Revealed Preference(SARP): 直接+间接显示偏好
- 若选择满足SARP,那么就总有可能找到满足最优化行为的偏好
- SARP 是使能观察到的选择与消费者选择的经济模型相一致的充分必要条件
- Index
- base period time
- Pasche quantity index:
- Laspeyres quantity index:
- if 消费者在 时期比 时期更好
- if 消费者在 时期比 时期更好
- price index 采用相似的方法定义
- (这里是价格指数) ,消费者在 时期比 时期更好
- 消费者在 时期比 时期更好
slutsky equation
- Hicks substitution effect: keeping purchasing power constant
- substitution effect must be negative
- called the compensated demand curve
- slusky substitution effect: purchasing power fixed
- substitution effect: 两种商品交换比率的变化引起的需求变化(转动前后的最佳选择带来的 )---sometimes called compensated demand
- 引起的需求变动方向总与价格变动的方向相反
- income effect: 购买力提高引起的需求变化(移动前后的最佳选择带来的 )
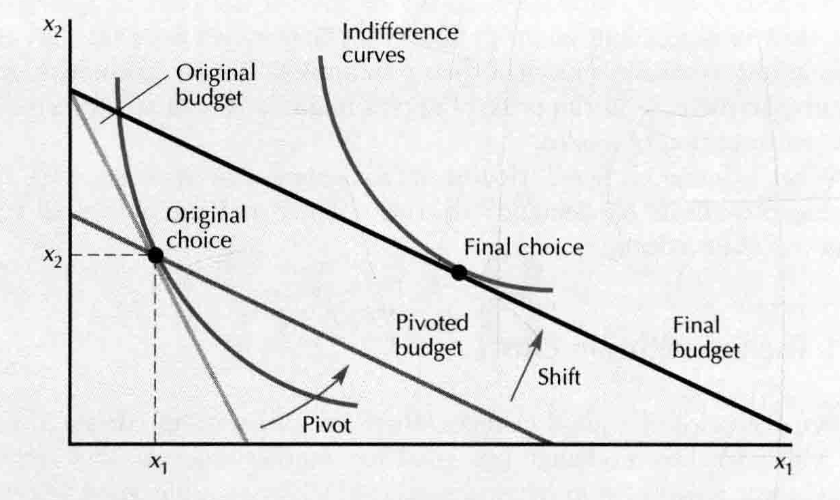
- slutsky identity:
- 替代效应总是负的,收入效应不一定
- rates of change: ( )
- Law of demand: demand for a good increases when income increases, the demand for that good must decrease when its price increases
- perfect complements: substitution effect is zero
- perfect substitutes: entire change in demand is due to the substitution effect
- quasilinear preference: income effect is zero
buying and selling
- cosumer starts off with endowment:
- gross demands / net demands / net supply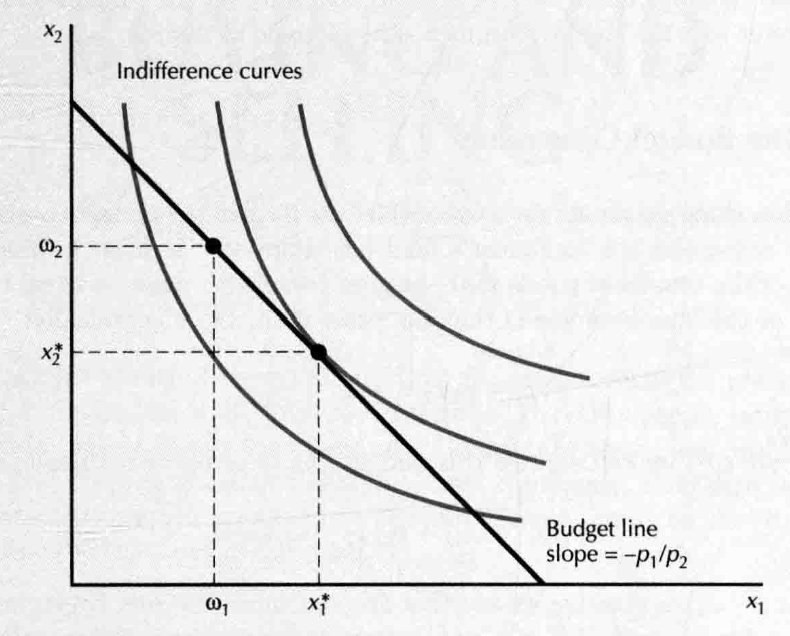
- changing the endowment:
- price changes: budget line pivot around the endowment
- consumer remains supplier and price decrease: welfare declined, switch to a buyer, we just don't know.
- price increase, consumer is a buyer: welfare declined, switch to a supplier, we don't know.
- price decrease, consumer initally a buyer---remain buyer
- offer curves:
- p change, combination of both goods that maybe demanded by a consumer
- always pass through the endowment
- Slutsky equation
- endowment income effect: suppose money income(价格未发生变化时,通过endowment挣得的钱) doesn't change, 计算价格变化前后,需求的变化。
Labor Supply
- nonlabor income, amount of consumption, price of consumption, wage rate, labor supplied
- amount of labor time, amount of consumption the consumer would have without working, is leisure, and the eqation:
- wage rate: opportunity cost of leisure.
- right side of this budget constraint: full income / implicit income(value of consumer owns); measured income: receives from selling off time
- labor supply: using slusky equation:
- 方程的第一项是负的,第二项是正的,造成了模棱两可的情况。当工资率增长时,劳动者的劳动时间先增大,后减小。
- Backward-bending labor supply:
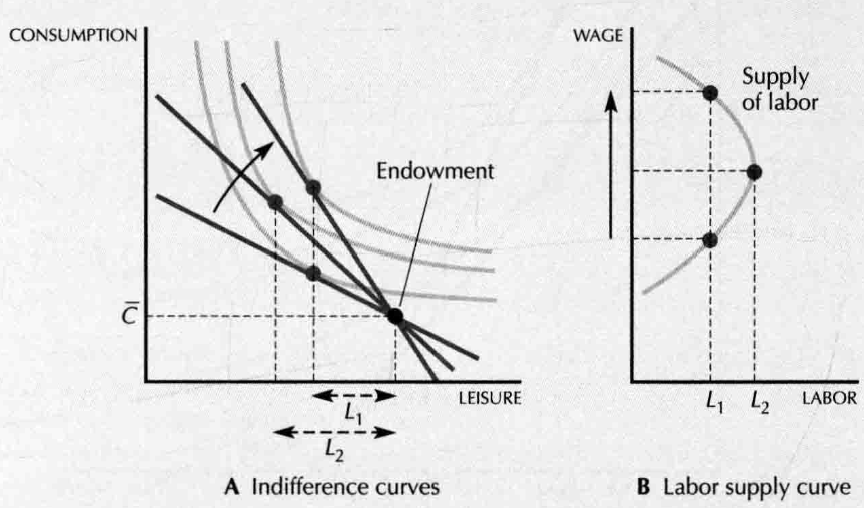
- Overtime wage increase results in a increase in labor supply and straight wage increase results in a decrease(maybe) in labor supply.
consumer's surplus
- consumer's surplus / net consumer's plus: (消费者放弃对某种商品的全部消费,而必须补偿给他的货币量)
- be careful with consumers' surplus
- 对拟线性效用,可以用需求曲线下的面积测度消费者效用,对非拟线性,也是一种合理的测度
- when price change, there are two loss: R: having to pay more/less for the unit continues to consume, T: measures the loss from the reduced/increased consumption.
- Compensating Variation: 价格变化后,要使消费者境况与价格变化以前的境况一样好,需要补偿多少货币。
- Equivalent Variation: 价格变化之前,需要从消费者那里取走多少货币,才能使他的境况与价格变化之后的一样好。 (注意解上面那两个的时候,要用效用一致作为解题的条件)
- 拟线性情况下, (最后一项是消费者剩余的变化)
- Producer's Surplus: area above the supply curve
- net producer's surplus: 出售得到的货币量和他愿意换取的最小货币量之间的差额
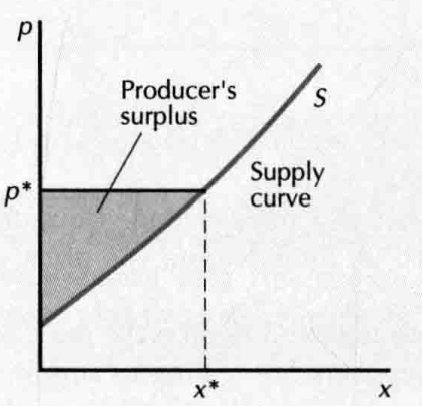
- net producer's surplus: 出售得到的货币量和他愿意换取的最小货币量之间的差额
market demand
- market demand / aggregate demand
- inverse demand function: emphaize price as a function of quantity, measures the marginal rate of substitution or the marginal willingness to pay
- intensive margin: 价格变动时,消费者每个都买,但有的多有的少
- extensive margin: 价格变动时,消费者决定要不要买某物
- elasticity:
- price elasticity of demand
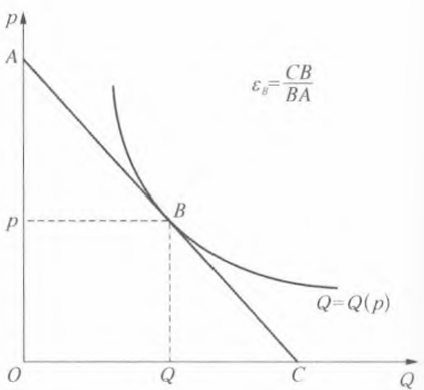
- absolute greater than 1 --- elastic demand
- less than 1 --- inelastic demand
- -1 --- unit elastic demand
- has subsititutes---curve responsive to price changes
- price elasticity of demand
- Revenue:
- elastic demand --- 价格上升收益减少
- inelastic demand --- 价格上升收益增加
- never set a price where demand was inelastic
- constant elasticity demands
- if price elasticity of demand=-1
- 公式 &
- Marginal Revenue
- Income Elasticity
- income elasticity of demand:
- normal good: 为正值
- inferior good: 为负值
- luxury good:
- expenditure share of good
- weight average of income elasticityies is 1(on average)
equilibrium
- market supply curve / market demand curve
- 经济主体接受不受它们控制的价格:competitive market(市场价格不受主体的影响)
- equilibrium price: ��达成了某种意义上的稳态
- 或者
- special cases:
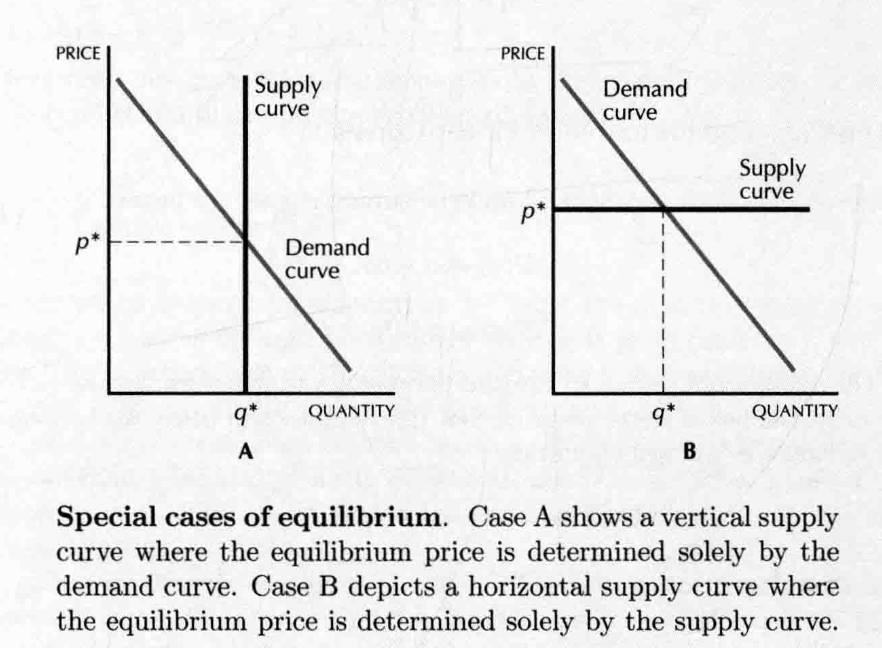
- when demand and supply curves shift to the left/right by the same amount, the equilibrium price will remain unchanged.
- quantity taxes: if is the amount of quantity tax per unit sold: (供给者 / 需求者谁支付税收不重要,只要有人付就行)
- 消费者购买商品花费的费用与征税的方法无关。
- ,移动需求曲线 / 供给曲线就行
- 补贴:
- value tax:
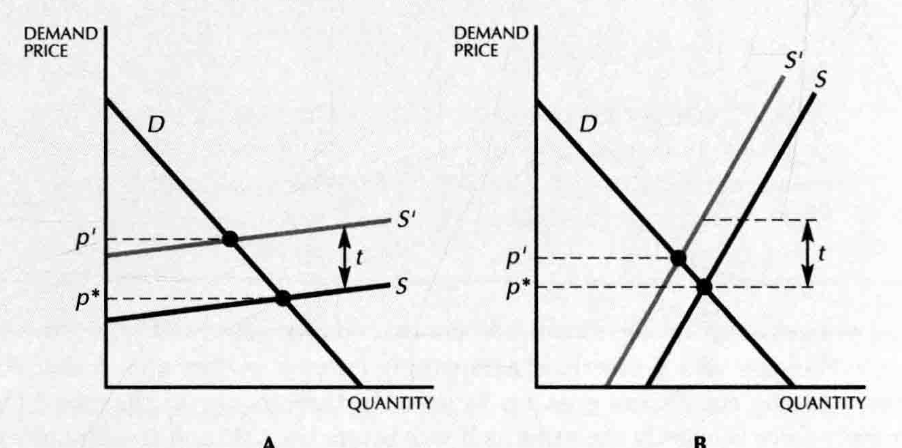
- 税收到底是谁付?(Passing Along a Tax)
- 收税之后, 向上提
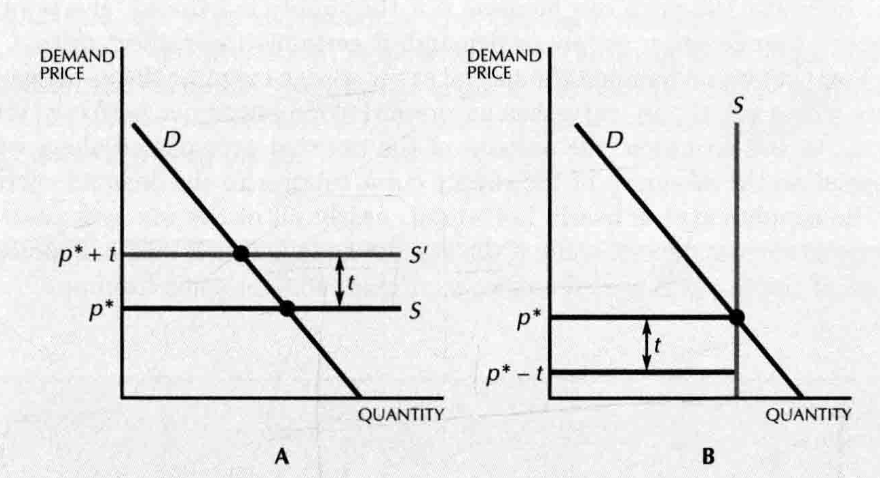
- perfectly elastic: 税收由消费者承担 ,均衡价格为 ,供给者获得
- perfectly inelastic: 税收由供给者支付,需求者支付 ,供给者得到
- between the two:
- 收税之后, 向上提
- Deadweight Loss of Tax
- Picture
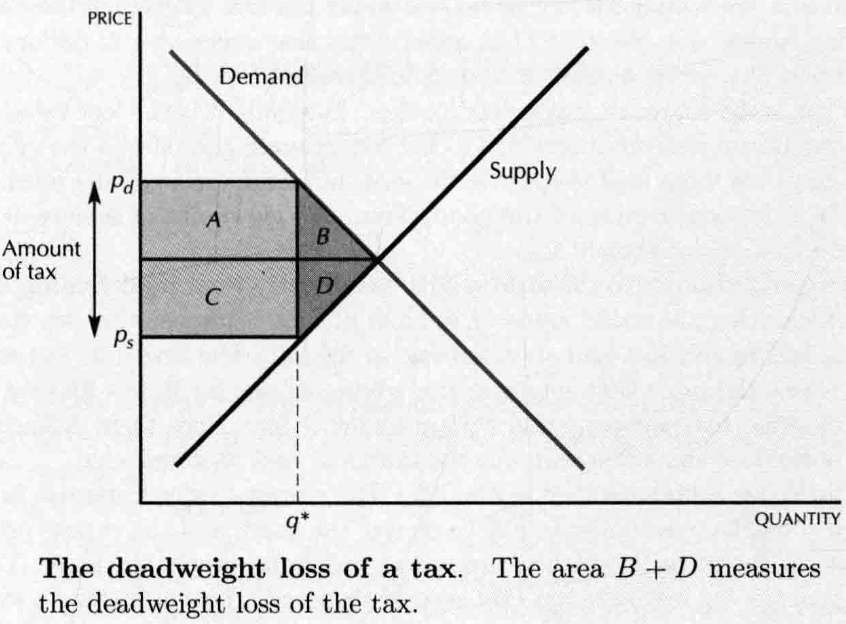
- loss in consumers' surplus:
- loss in producers' surplus:
- gain in government revenue:
- deadweight loss / excess burden: (lost value to the consumers and producers due to the reduction in the sales of the good)
- waiting in line is a form of deadweight loss
- Picture
- competitive market produces a Pareto efficient amount of output
提示
- 偏好集的凹凸与无差异曲线的凹凸不同
- 不喜欢并且可以扔掉相当于中性品
- 无差异曲线分为形状与方向,判断是否well-behaved需要计算斜率是否恒递减
- 超过配给量 时超过的部分征税
- 用另一商品替代,需满足
- 注意在哪里取最优值
- 预算集内外的消费束无法比较,线段上没购买的消费束无法与预算集内外的消费束比较
- Labor 曲线一定是与劳动有关的
- 提供免费的啥
Neoclassical Firms
Technology
- Input to production factors of production
- capital goods are those inputs to production that are themselves produced goods
- financial capital / physical captial
- techonological constraints
- production set
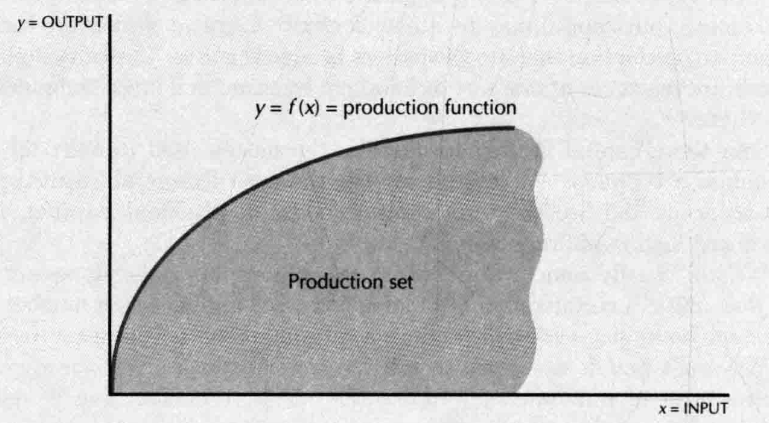
- Isoquant -- similar to indifference curves
- production set
- example of technology isoquant
- Fixed proportions:
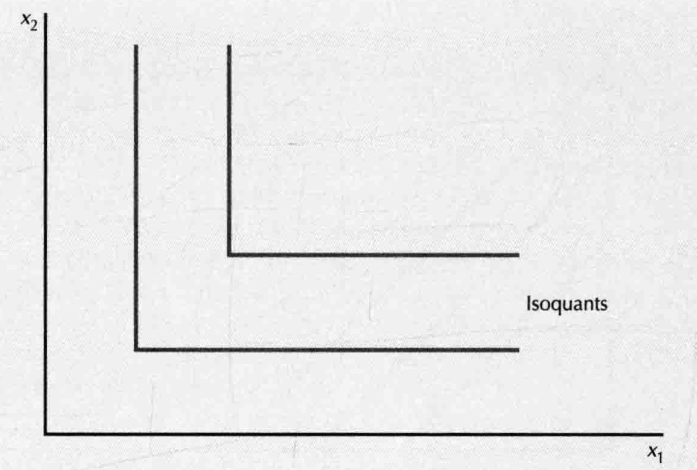
- Perfect Substitutes
- Cobb-Douglas:
- Fixed proportions:
- Properties:
- monotonic: 增加投入的数量会生产出至少比原来更多的产品(or property of free disposal)
- convex
- Marginal Product
- for factor 1
- 与
- Technical Rate of Substitution
- 放弃要素1 获得多少要素2
- law of diminishing marginal product: 增加一个投入其他投入不变,边际产品如何变化
- diminsishing technical rate of substitution: 增加一种收入的数量,另一种减少,让产量保持不变,等产量线的斜率如何变化
- long / short run
- short run some factors fixed at predetermined levels, production function for the short run
- long run all the factors of production can be varied
- short run some factors fixed at predetermined levels, production function for the short run
- returns to scale
- constant returns to scale:
- increasing returns to scale:
- decreasing returns to scale: (忘记了某些投入)
Profit Maximization
- individual producer take the prices as outside their control a competitive market
- profits:
- oppotunity costs: 劳动用于某种用途,就丧失了其他用途的机会
- fixed/variable factor/ quasi-fixed factors(只有厂商决定生产一定单位的产量时才需要支付成本的要素)
- in the long run all factors are variable factors, but in the short run firm could make negative profits
- short-run profit maximization:
- 是实现利润最大化的数量, ,
- isoprofit lines: ,截距是 是利润和固定成本之和,只有 与 的变化会造成影响
- long-run profit maximization
- ,所有要素都可以变化
- (价格 利润最大化选择)
- factor demand curves: 价格不同,找到 ,利润最大化时的产量: ,利润
- inverse factor demand curve:
- 所有产量水平上都具有不变的规模报酬的一家竞争企业的情况下,企业长期利润水平是零(当然此时并不符合前面的条件)
- WAPM(Weak Axiom of Profit Maximization)
- 有 期和 期,在生产函数不变的情况下,在任意期价格,采用该期的生产计划所获得的利润大于其他期的利润
- 可以通过两条等利润线构造一个令两处都是利润最大化选择的技术。
- 利润最大化 成本最小化
Cost
Cost Minimization
- Cost Minimization
- ,such that
- cost function(取决于 的值): (当要素价格 时,生产 单位产量的最小成本),记为
- 当 变化时,获得一群 isocost lines
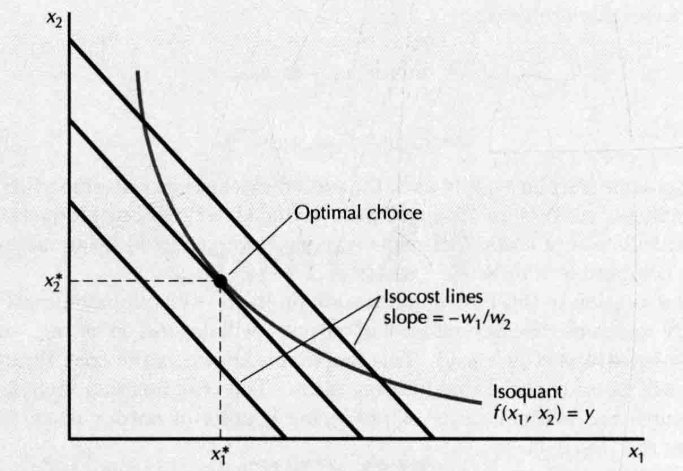
- 相切条件:
- 若处在成本最小化的点上
- 与消费者问题不同,消费者问题中的约束是预算约束线,生产者问题中的约束是等产量线(技术约束)
- 成本最小的要素选择 ,称为 conditional factor demand functions/derived factor demands(给定产量下成本最小化的选择)
- Cobb-Douglas technology(Minimizing Cost): ( )
- Revealed Cost Minimtion
- WACM(Weak Axiom of Cost Minimization)不同要素价格时,选择都是成本最小化的选择
- 考虑到规模报酬,想要研究成本与产量的关系: average cost function:
- 若规模报酬不变:
- increasing return to scale: AC declining
- decreasing returns to scale: AC increasing
- 不考虑要素价格,成本仅仅是产量的函数
- Long-run and Short-run cost
- short-run cost function: 只有可变生产要素可以调整的情况下生产某产量的最小成本
- , such that
- ,
- 由 和 决定
- long-run cost function: 一切可调的时候……最小成本
- , such that
- ,
- 相当于要素2固定在使长期成本最小化的水平上时的最小成本
- short-run cost function: 只有可变生产要素可以调整的情况下生产某产量的最小成本
- Fixed Costs: 不管是否生产都必须支付的成本 / Quasi-fixed costs: 只要生产就必须支付
- 二者均与产量无关
- 长期不存在 fixed costs, 但是容易产生 quasi-fixed cost
- Sunk Costs: 一旦支出就不会收回的成本
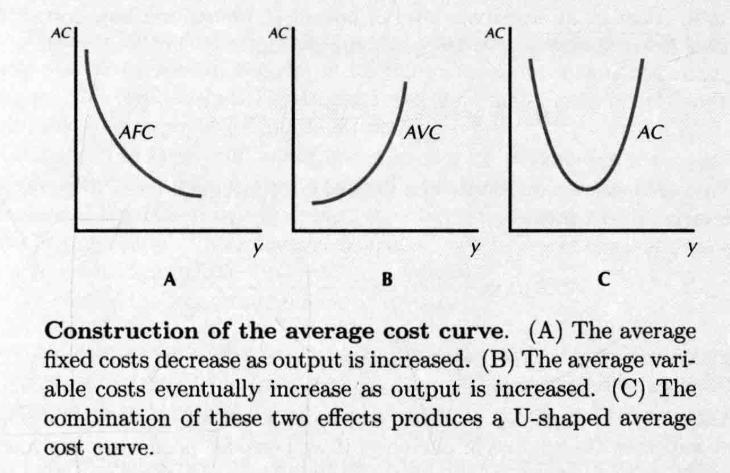
Cost Curves
-
- average variable costs
- average fixed costs
- 当平均可变成本比较高的时候,由于存在不变要素,最终制约生产过程
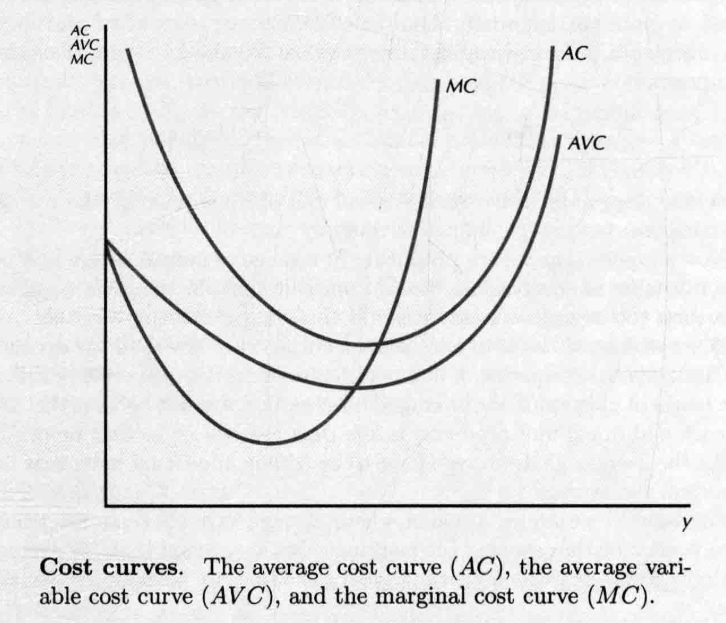
- Marginal Costs
- 产量的变动引起成本的变动
- 成本变动量与产出变动量之比
- average variable costs decreasing, marginal costs less than the average variable costs, 反之亦然(边际成本拉动平均成本)
- The marginal cost curve passes through the minimum point of both the average variable cost and the average cost curves
- Marginal Cost vs Variable Cost
- (微积分关系)
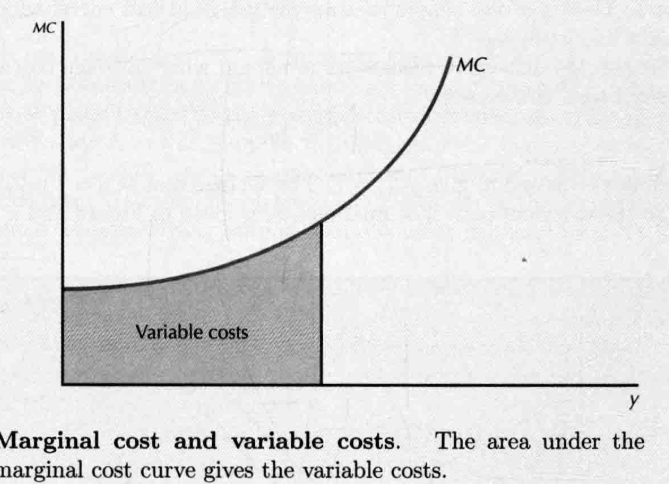
- (微积分关系)
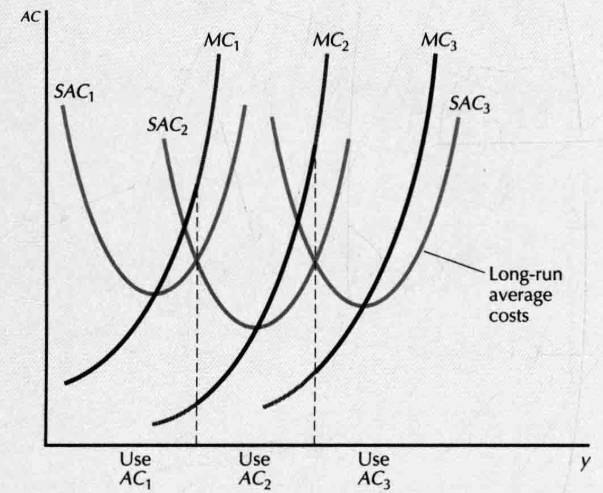
- Marginal Cost Curves for Two Plants: 如果厂商拥有两家工厂,那么二者的边际成本相当(总的边际成本是水平方向上的加总)
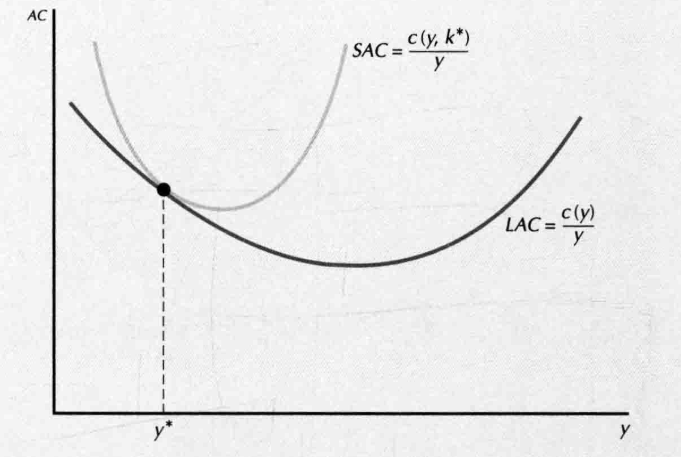
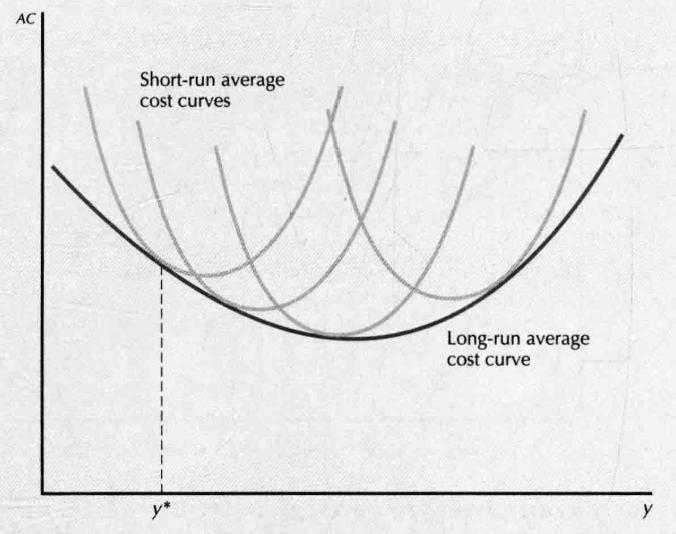
- Long-run Costs
- 长期不存在不变成本
- 某个产量 , 表示生产 的最优规模(也就是对应的短期不变成本),则有
- 对所有产量 ,有 ,在特定产量水平 上
- ,
- short-run average cost curve(SAC) always lies above the long-run average cost curve(LAC) and they touch at one point
- Marginal Costs
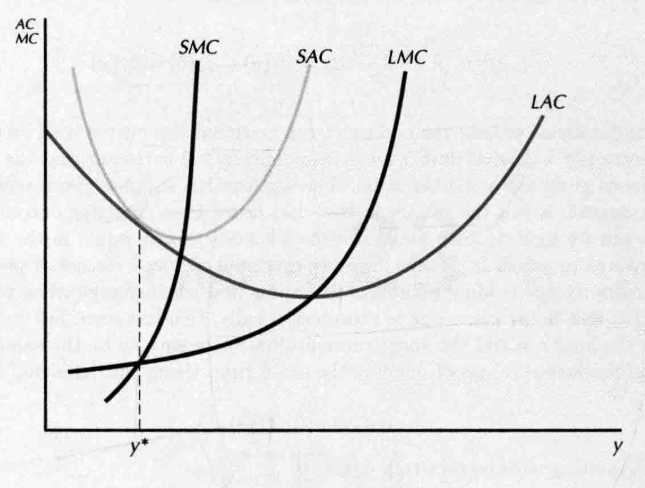
- Marginal Costs
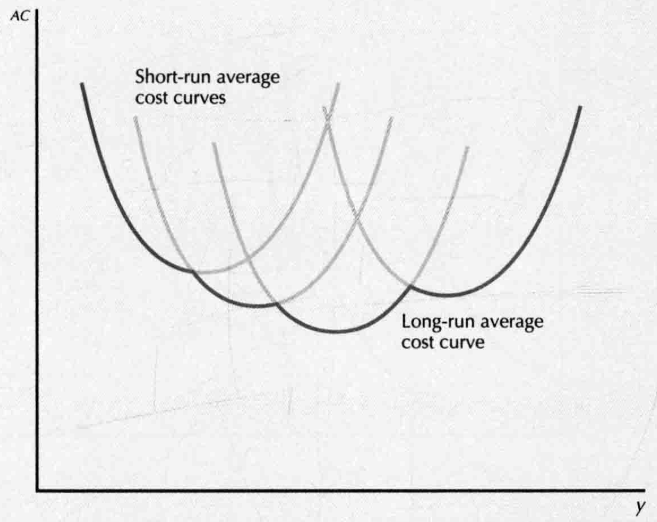
- discrete levels of plant size: only have several choices, long-run average cost curve is the lower envelop of the short-run average cost curves
- Marginal Costs
- Marginal Costs
Firm Supply
- Constraints that firm faces
- technological constraints(summarized by the production function) economic constraints(summarized by the cost function)
- market constraint: 公司只能卖出消费者需要的数量的东西( demand curve)
- market environment: pure competition, each firm assumes that the market price is independent of its own level of output
- 很多小厂商生产同质的商品
- 几家厂商生产易腐烂的商品
- 市场上只有两家厂商,但一家厂商无论什么情况都按照不变价格出售商品
- demand curve facing a competitve firm
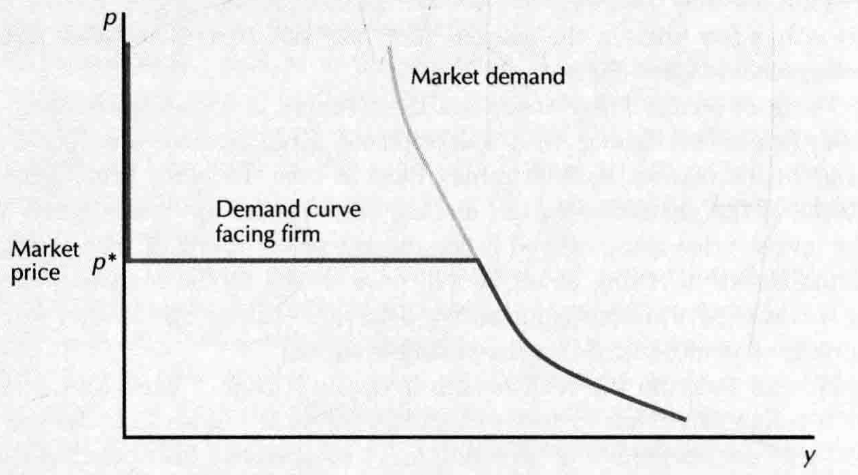
- market demand curve depencs on consumers' behavior; demand curve facing a firm not only depends on consumers' behavior but also depends on the behavior of the other firms
- Supply decision of a competitive firm: ,选择的产量水平刚好是边际收益等于边际成本处也即 (necessary condition but not sufficient condition)
- 价格等于边际成本的产量有好几个?——选择边际成本递增的那个
- 有时厂商的最佳选择是零产量 也就是 边际成本曲线位于平均可变成本曲线以上的部分才是供给曲线的可能点
- 综上:在边际成本曲线向上倾斜且位于平均可变成本曲线以上的部分组织生产。
- 市场价格能够反映行业中每一家厂商的边际成本。
- profits and producer's surplus
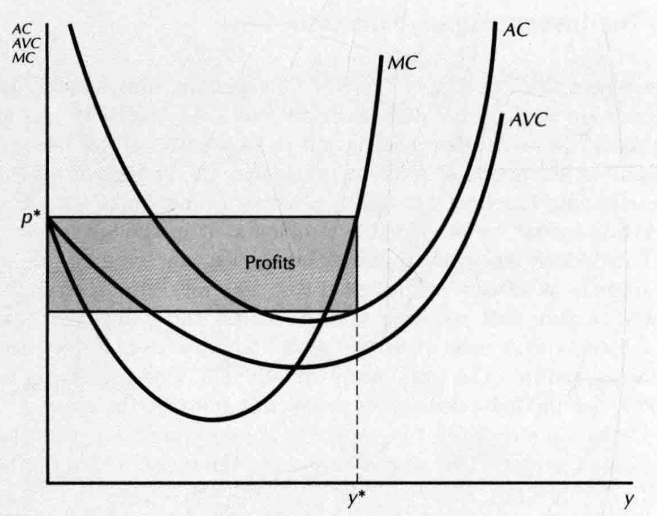
- profits
- producer's surplus
- 其他方法:
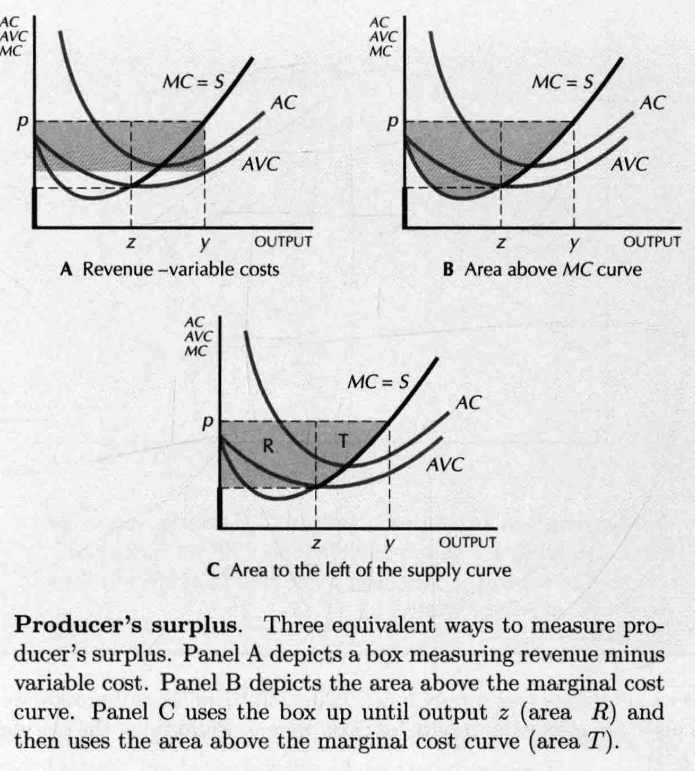
- change in producer's surplus
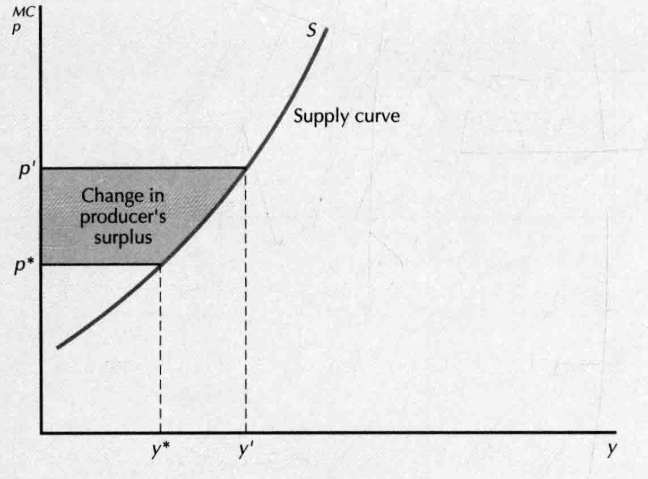
- 由于不变成本不变,那么生产者剩余的变动量恰好等于利润的变动量
- Long-Run Supply Curve of a Firm
- long-run supply curve:
- short-run supply curve:
- 短期: 不变;长期: 调整到最优水平
- 因此,长期的供给曲线和短期的相交,且长期的对价格更敏感(有更多的调整空间)

- 由于长期的时候厂商的自由度很高,故长期均衡中厂商的利润至少等于 :
- 长期内价格必须至少等于平均成本。
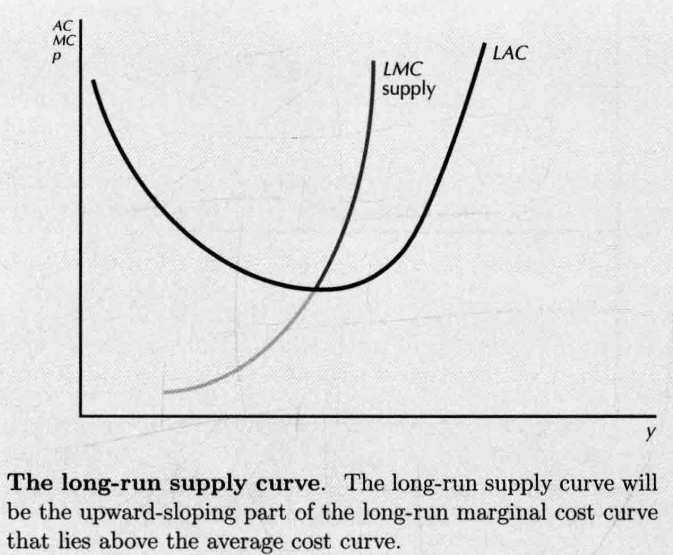
- 长期内价格必须至少等于平均成本。
- long-run constant average costs
- 平均成本不变的时候,长期边际成本曲线与长期平均成本曲线相同

- 厂商愿意供给任意数量的产出; 厂商愿意供给任意大数量的产出; 供给数量为
- 平均成本不变的时候,长期边际成本曲线与长期平均成本曲线相同
Industry Supply
- Short-Run Industry Supply:
- market supply curve
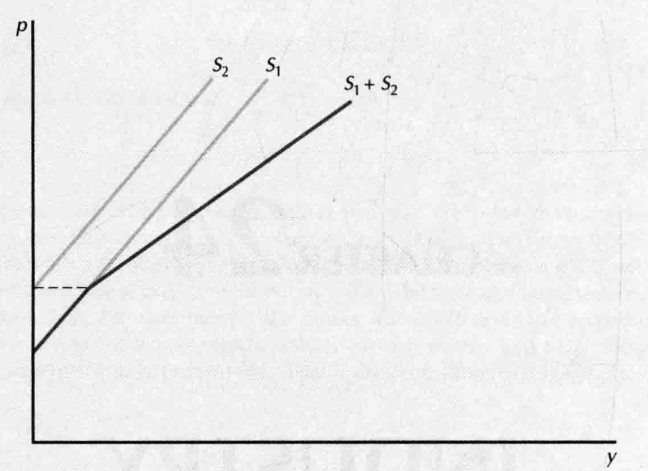
- 供给曲线=需求曲线(Industry Equilibrium),得到均衡价格 ,从 出手,看每个厂商:
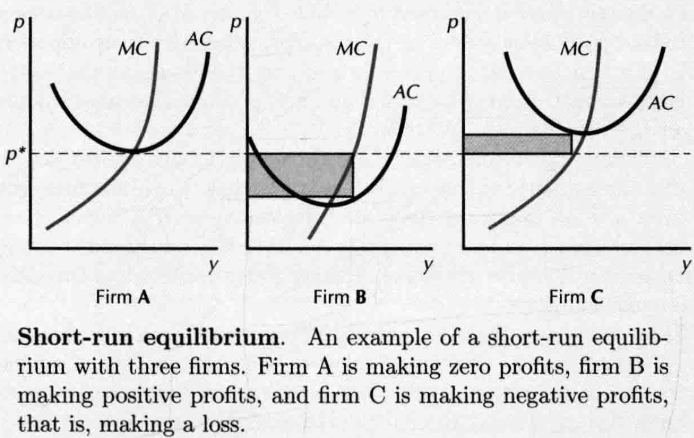
- 高于平均成本曲线意味着利润为正值
- market supply curve
- Industry Equilibrium in the Long Run
- two long-run effects: acquiring different fixed factors / entry and exit phenomena(free entry)
- 设行业内所有厂商都有完全相同的长期成本曲线 ,成本最低时的产量 。 平均成本的最低额 市场可��以索要的最低额。
- the maximum number of competitve firms this industry can support:
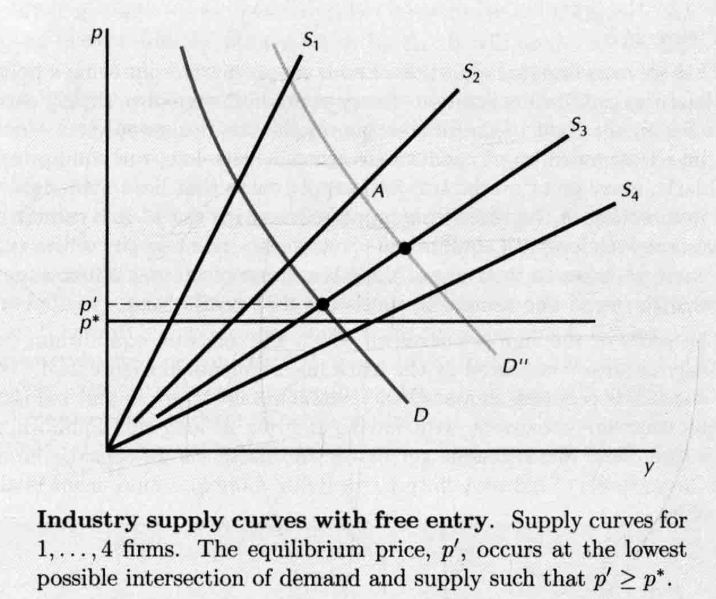
- The long-run supply curve
- 排除供给曲线低于 的点,以及高于 ,但此时可以有更多家厂商进入的点,所以长期供给曲线如下图所示
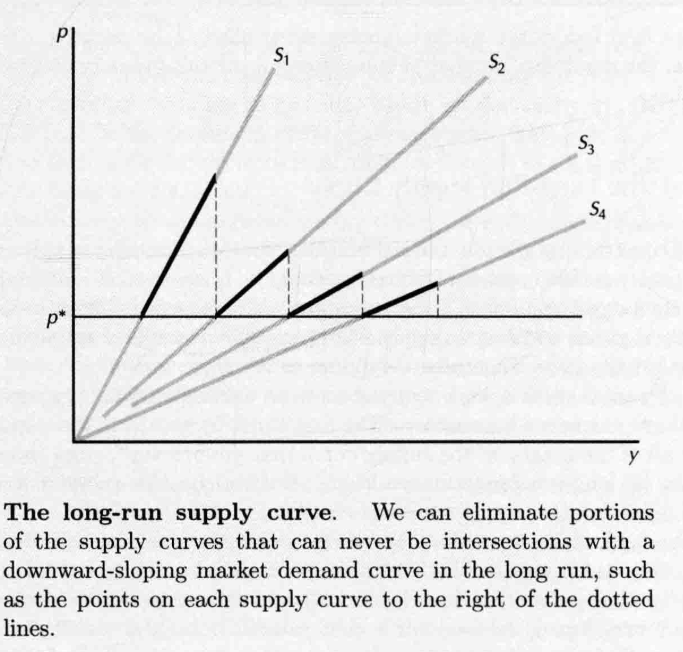
- 当市场上有很多厂商的时候……供给曲线的斜率将变成
- 排除供给曲线低于 的点,以及高于 ,但此时可以有更多家厂商进入的点,所以长期供给曲线如下图所示
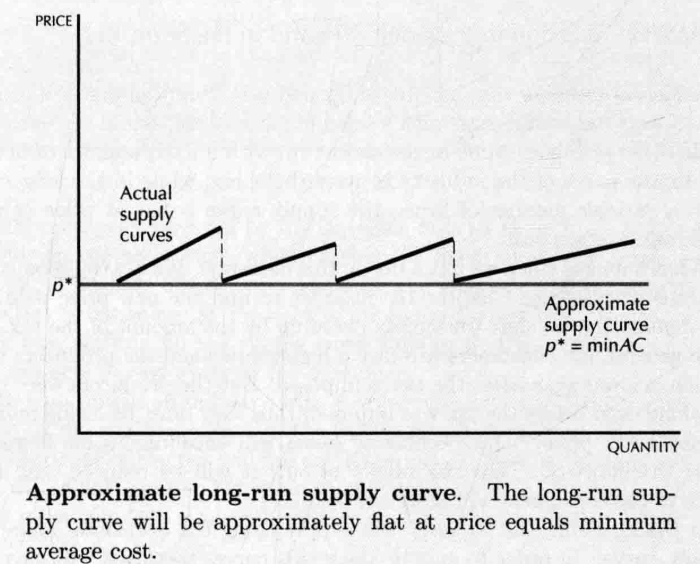
- 若一个可以自由进入的行业利润非常高,长期来看利润会趋向于 ,长期平均成本在价格等于最小平均成本处是水平的(是规模报酬不变的厂商具有的长期供给曲线)
- Taxation in the long run and in the short run
- 从短期到长期区别在于厂商可以自由进入/退出行业。
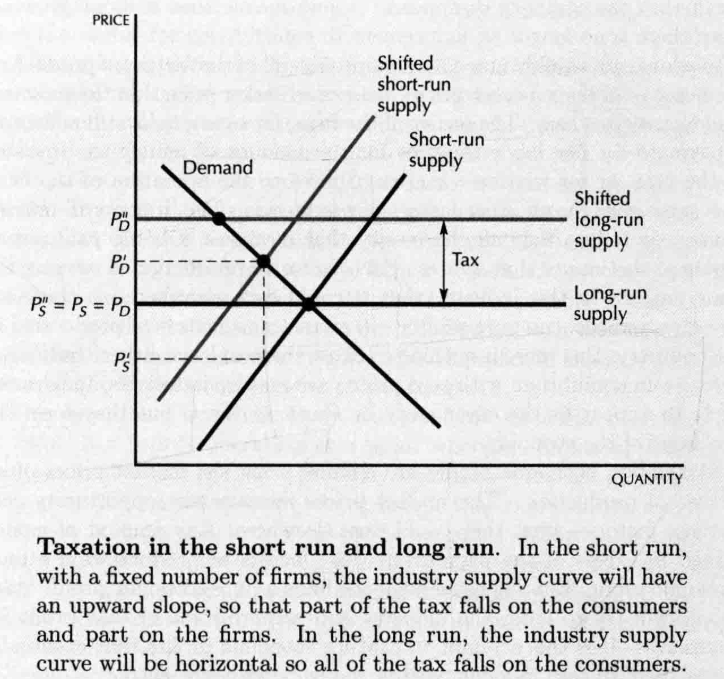
- 自由进入的行业中,征税首先提高消费者价格,另一部分税收由生产者承担,但长期来看全部税收都会由消费者支付。
- 从短期到长期区别在于厂商可以自由进入/退出行业。
- Zero Profits
- 并不是这个行业不赚钱,而是一切生产要素(包括劳动时间之类)按照市场价格支付,每种生产要素在该行业得到的报酬和其他行业能得到的报酬相同。
- 不存在额外的报酬
- (pure economic profit)纯经济利润:厂商赚得的超过生产要素报酬的任何货币量 在一个自由进入的竞争行业中,这种谋取经济利润的动机是的经济利润最终趋于
- Fixed Factors and Economic Rent
- 一些有行业门槛的行业有可能在长期内获得利润吗?不可能。我们需要考虑这些“门槛”本身的市场价值。若农场主扣除生产成本之外得到了一笔 美元的利润,那么农场主这块土地的年租金的价格也恰好是 美元。(这与历史成本没有关系,因为这里我们计算的是机会成本(oppotunity cost)
- 只要有不变要素妨碍进入某行业,这样的要素就该有一个均衡的价格。
- Economic Rent: 一些物品的价格(比如石油)高于获得石油必须支付的最低价格的部分
- 对一块土地而言:
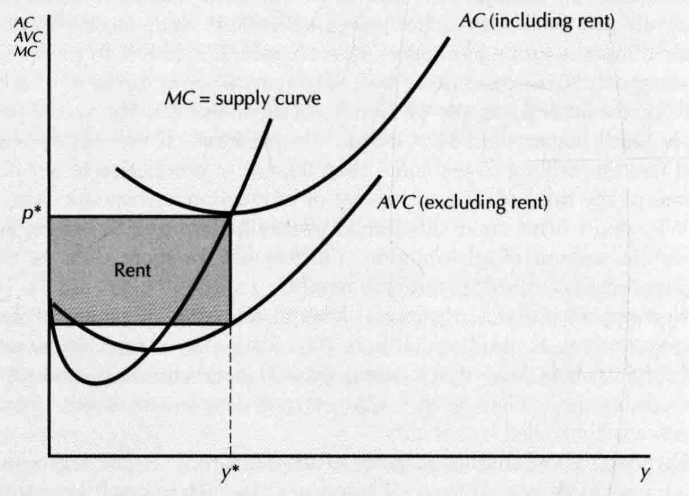
- 如果我们能够准确地计算土地的价值,那么从事农业经济生产的利润恰好为
- 均衡价格决定租金,而不是租金决定均衡价格
- 对一块土地而言:
- Rental Rates and Prices
- 前面说到生产要素的价格之时,都是使用单位时间的价格进行衡量,当考虑直接售卖这些生产要素之时,这时的均衡价格就是收益流的现值。
- 发放更多的执照会使得现有的这些执照贬值,从而带来这些执照持有者的经济损失。
- Rent seeking: efforts directed at keeping or acquiring claims to factors in fixed supplies
- Carbon Tax VS Cap and Trade
- 设有两个企业,则最小化问题
- Carbon Tax: 设定碳税率 ,就可使目标碳排放量为
- Cap and Trade: 设一张排放许可证价格为 ,则最终会达到
- 若政府选择价格并出售许可证:等同于碳税制度
- 若政府选择排放量让企业定价/依据规则向企业办法许可证,则是限额交易制度,但企业会额外付出一些寻租成本。
Monopoly
- monopoly: industry structure when there is only one firm in the industry
- Maximizing Profits
- 是市场的反需求曲线,利润最大化问题 ,也可以写成 ,其中 是收益函数。
- 最优化条件
- 对垄断厂商:增加产量 之后,收益影响为 ,边际收益 ,用弹性公式 ,在充分竞争的时候,��需求曲线是水平的 ,因此对于竞争厂商而言,最优化条件就是价格等于边际成本
- 但对于垄断厂商而言 减产就会增加收益,此时总成本也减小,利润必然增加。所以利润最大化的点一定出现在 的地方
- Linear Demand Curve and Monopoly
- demand curve
- revenue function:
- 图
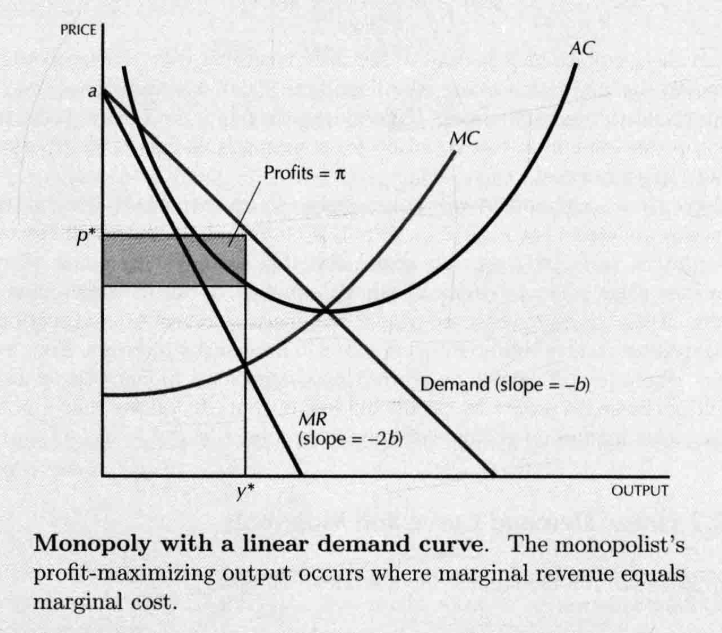
- 另一种描述方式: Markup Pricing
- market price is a markup(depends on the elasticity of demand) over marginal cost
- 当 是常数时
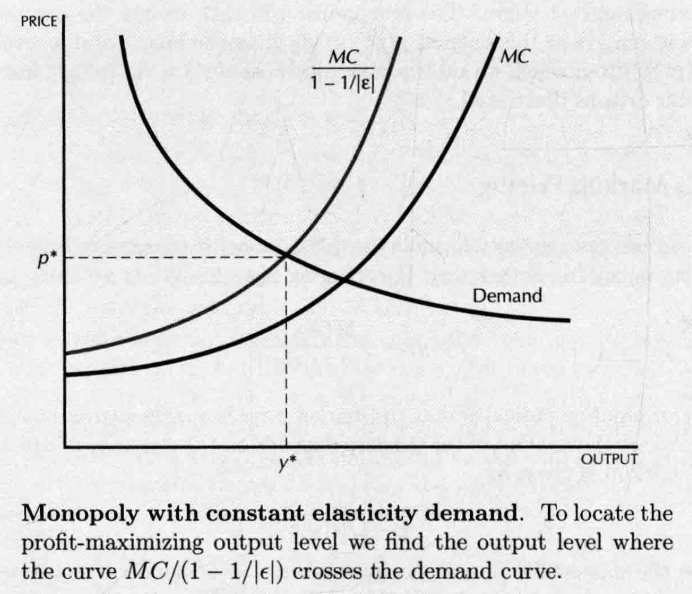
- Taxes on monopolist 边际成本不变:
- 线性需求曲线:价格的上升幅度等于税额的一半
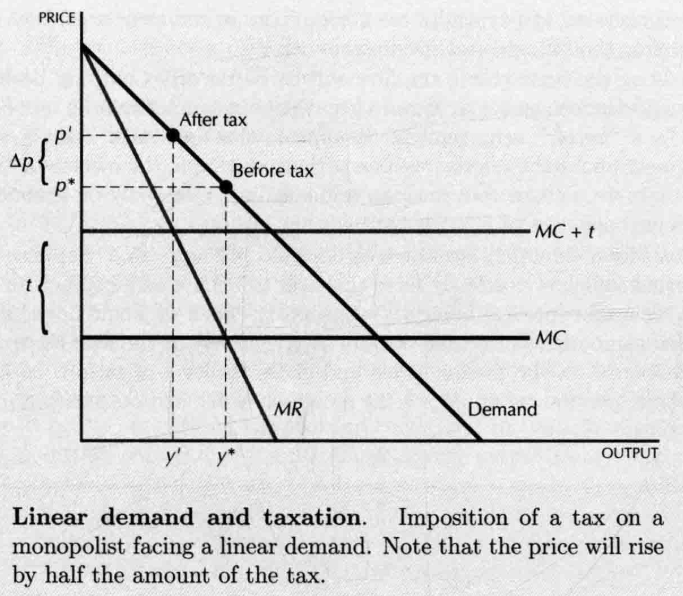
- 不变弹性需求曲线的垄断厂商 , 价格上升的幅度大于税额
- 若税收是利润税,利润最大化问题是 ,其中 是利润税,完全的利润税不会对垄断厂商的产量选择产生影响
- 线性需求曲线:价格的上升幅度等于税额的一半
- 垄断行业在价格大于边际成本的点经营,与竞争厂商相比,垄断厂商的价格较高,产量较低。厂商的情况较竞争时好,但消费者的境况更差。
- 但垄断并不是能够达到帕累托最优的情况。
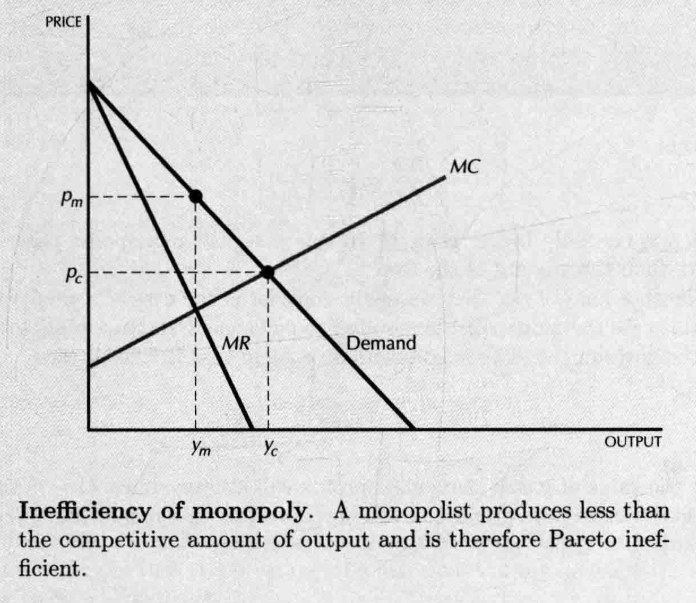 在垄断产量水平 ,存在一个消费者,愿意出 ( )的价格支付 单位的额外产量,这时,消费者得到了产品,厂商获得了 的利润,是一种“帕累托改进”
在垄断产量水平 ,存在一个消费者,愿意出 ( )的价格支付 单位的额外产量,这时,消费者得到了产品,厂商获得了 的利润,是一种“帕累托改进”
- 垄断厂商需要考虑增加产量对边际内单位收益(inframarginal units)的影响。它们总是愿意按比现行价格更低的价格出售额外单位的产量,只要这样做不会让边际内单位产量的价格降低
- Deadweight Loss
- A: 垄断厂商最初销售的产品如今降价了,厂商的损失;消费者原来需要高价买的产品,现在需要低价买到,消费者获得的剩余;二者互相抵消】
- B:消费者从额外出售的产量中得到的剩余
- C: 出售额外单位产量获得的额外利润
- deadweight loss due to the monopoly
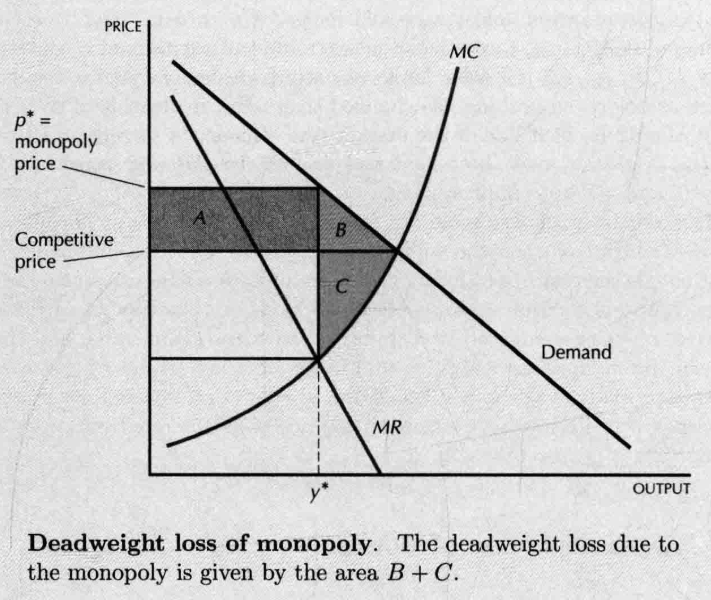
- 每生产一个额外产量,新增的“社会价值”就是价格与边际成本的差额。
- Natural Monopoly
- 在最有帕累托效率的时候,厂商可能会亏损
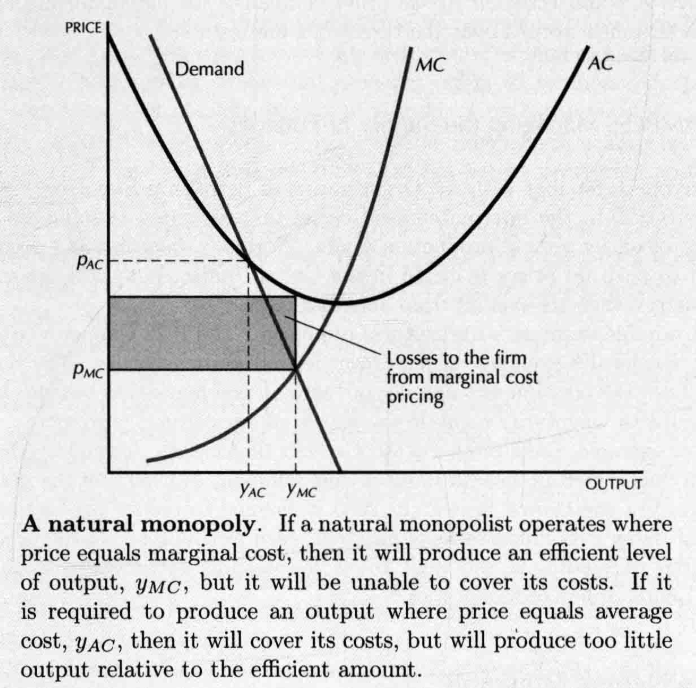
- 最有帕累托效率的点: (同时 与 的关系满足需求曲线)
- 至少能赚钱的点: (同时 与 的关系满足需求曲线)
- 一般出现在技术涉及大量固定成本,但边际成本比较小的时候
- 由政府管制,使得厂商的自然经营位置大概在 ,但确定厂商的成本比较困难
- 由政府经营,在价格等于边际成本处提供服务,或采取补贴,但确定自己的成本比较困难
- 在最有帕累托效率的时候,厂商可能会亏损
- What causes monopolies:
- minimum efficient scale (MES) vs the size of demand
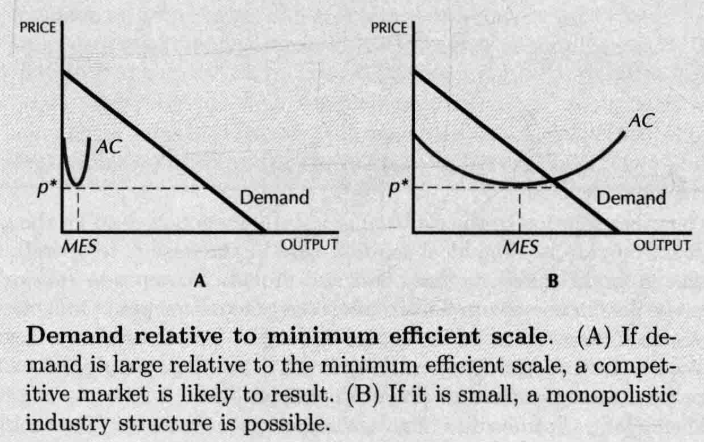
- several different firms in an industry collude and restrict output--organized as a cartel
- 主导厂商最先进入某个行业,有足够的成本优势(一旦有外来者,就狠狠降价,这样外来者就赚不到了)
- minimum efficient scale (MES) vs the size of demand
Monopoly Behavior
- 竞争市场:提价后,消费者转向其竞争者。
- 垄断市场:提价后,会失去一些消费者,但不是全部
- 拥有垄断势力的厂商拥有更多的选择权。
- Price Discrimination
- 垄断厂商不想生产额外产量,因为这样会降低全部产量的价格,但厂商可以按不同的价格出��售不同单位的产量,这就是价格歧视
- First-degree price discrimination(perfect price discrimination): 按照不同价格出售不同单位的产量,并且价格因人而异。
- each unit of good is sold to the individual who values it most highly
- 不存在消费者剩余,生产者得到了市场上的全部剩余。
- Second-degree price discrimination(non-lineaer priceing): 不同的产量之间存在价格歧视
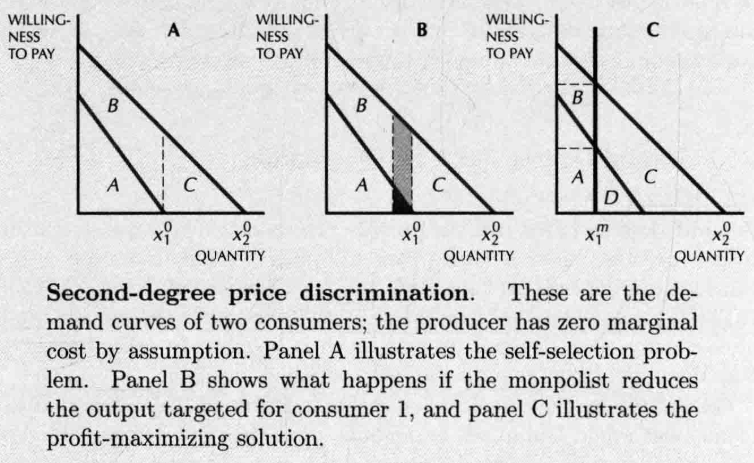
- 上图中的数量也可看作质量。垄断厂商会减少向低端市场提供的数量,以不损害高端市场的销售量。对于高端市场的消费者,低端消费者是有益的,因为没有低端消费者,高端消费者获得的剩余为零。
- 最优定价策略:在具有较高支付意愿的市场上索取高价,并在具有较低支付意愿的市场上销售低质量的产品。
- Third-degree price discrimination: 对不同的人按不同的价格,但每单位产量都按相同的价格出售(老年优惠,学生优惠)
- 利润最大化问题
- 最优解:
- 当 则有 具有较高价格的市场一定有较低的需求弹性。
- 如果一个厂商被迫对不同需求曲线的消费者以同一个价格出售产品的时候,它可能会放弃某个市场。
- Bunding 搭售
- 向不同的人销售商品时,价格是由具有最低�支付意愿的购买者确定的。搭售可以降低支付意愿的分散程度(若有 A 和 B 的套装,那么对 A 接收价格高,对 B 接收价格低/接受价格的这两类消费者,都可以接受套装稍高的价格,这样可以提高利润)
- Two-Parts Tariffs
- 人们愿意进入迪士尼乐园支付的价格,取决于他们必须为参与娱乐项目支付的价格
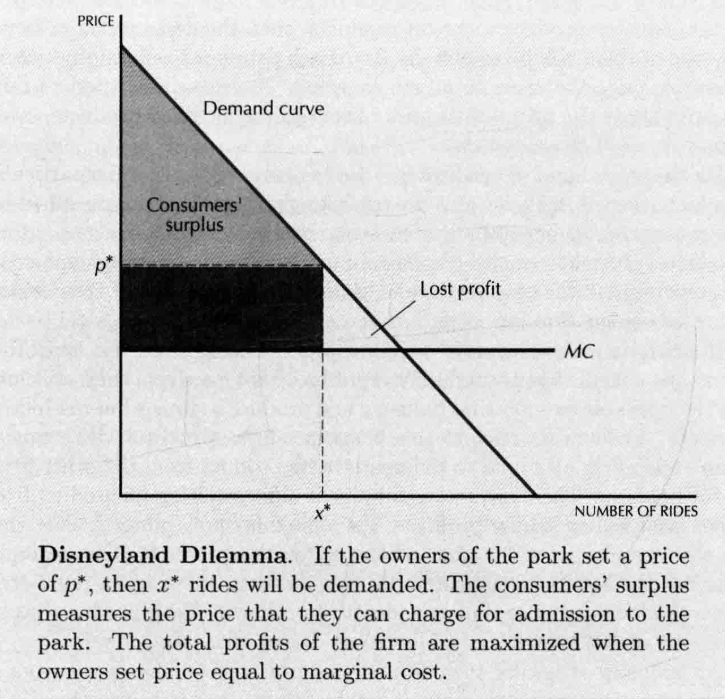
- 当乘坐娱乐项目的价格等于边际成本的时候,总利润实现了最大化,娱乐项目的边际成本低于对其单独收费所产生的交易成本。
- Monopolistic Competition
- 行业被看作生产的产品在消费者看来是相近替代品的所有厂商的集合
- 产品越差异化,越能将产品和行业中其他厂商的产品分开来,垄断力就越大。
- 这种行业结构称为 monopolistic competition
- 垄断竞争在自由进入方面的特征
- 最终的均衡
- 每家厂商都在按需求曲线上的价格和产量组合出售产品(在需求曲线上
- 给定需求曲线,每家厂商都在追求利润的最大化
- 新厂商的进入使得每家厂商的利润降到零(在平均成本曲线上,且需求曲线和平均成本曲线不可能相交,否则需求曲线在成本曲线上方, ,不满足零利润)
- 需求曲线和平均成本曲线必定相切。
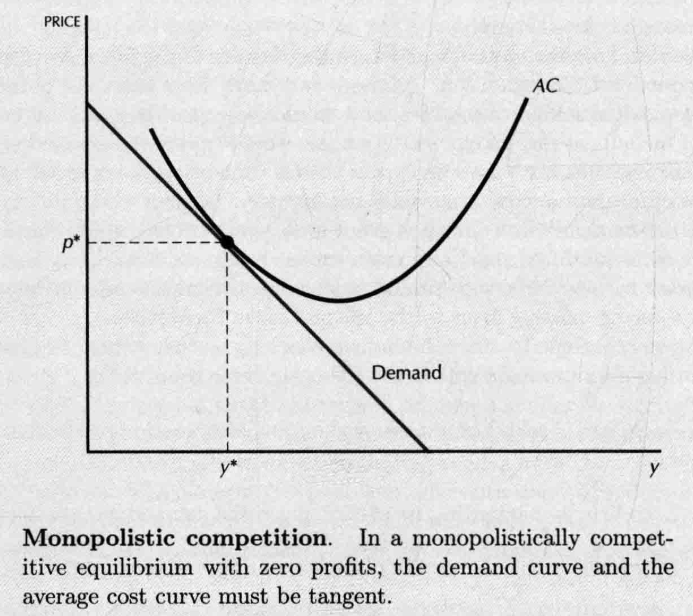
- 虽然零利润但是帕累托低效率的,价格大于边际成本时,增大产量就会增加利润。
- 利润和效率问题完全无关
- 增加产量,似乎提高了帕累托效率,但也使得市场上的产品种类减少,消费者的境况会变坏(更垄断了),所以不好说消费��者的境况是好是坏
- 最终的均衡
- Local Model of Product Differentiation
- competition for customers has resulted in an inefficient location pattern
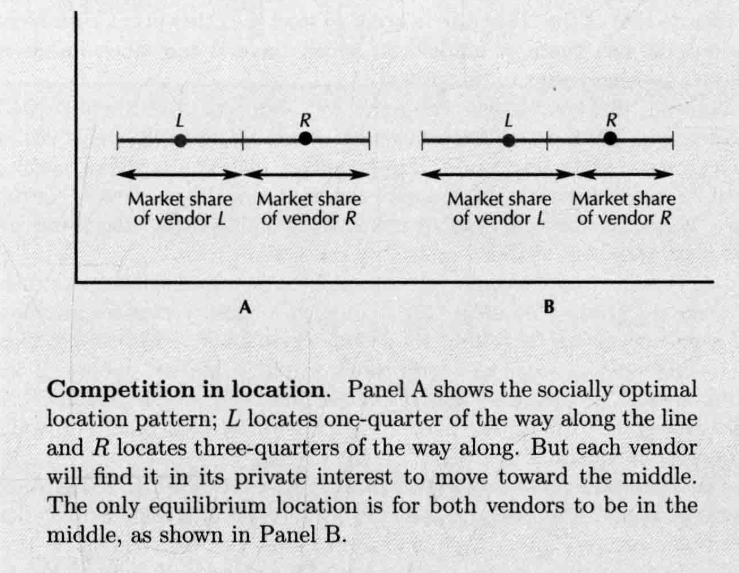
- monopolistic competition will result in too little product differentiation
- 但如果道路非常长(市场范围不重叠),就不会导致过度模仿的市场
- 每一家厂商都会投资创建独特的品牌。
- 如果海滨大道上有三个小贩,不存在均衡位置
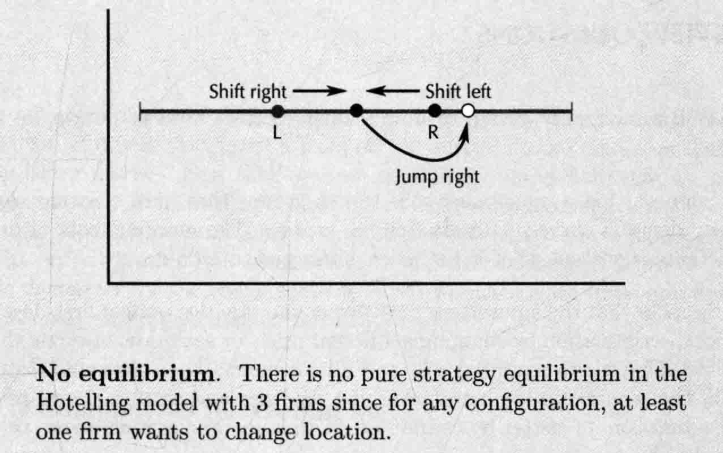
- 不过如果小贩更多,均衡情况就会出现
- competition for customers has resulted in an inefficient location pattern
Factor Markets
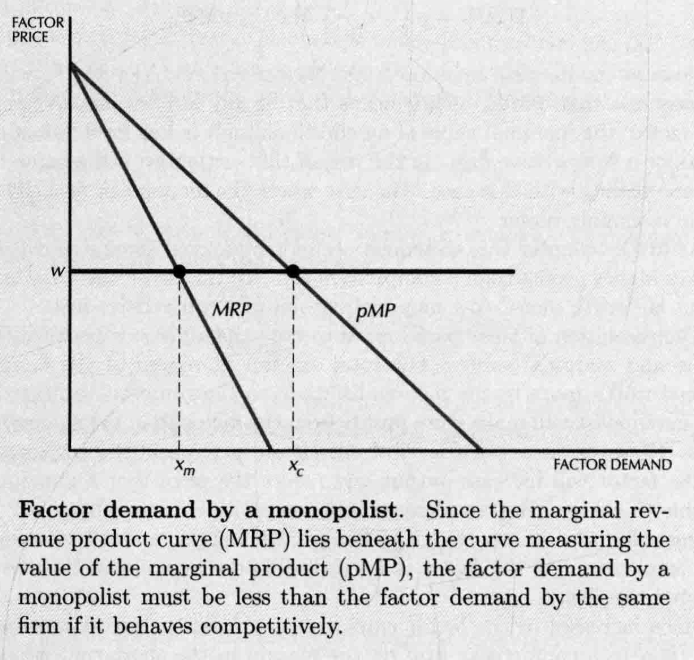
- 考虑厂商与生产要素的需求,探讨生产要素的增加如何影响厂商的收益。
- 边际产品
- 边际收益
- 边际产品收益:
- 竞争市场需求曲线弹性无穷大,边际收益恰好等于价格,于是边际产品收益等于边际产品价值
- 垄断的情况下,边际产品收益总小于边际产品价值。(注意这里的价值是边际价值,而非总价值)
- 垄断厂商通常会使用较少的要素来获得比较高的利润
- 设要素的价值是 ,那么
- 对竞争厂商而言
- 对垄断厂商而言
-
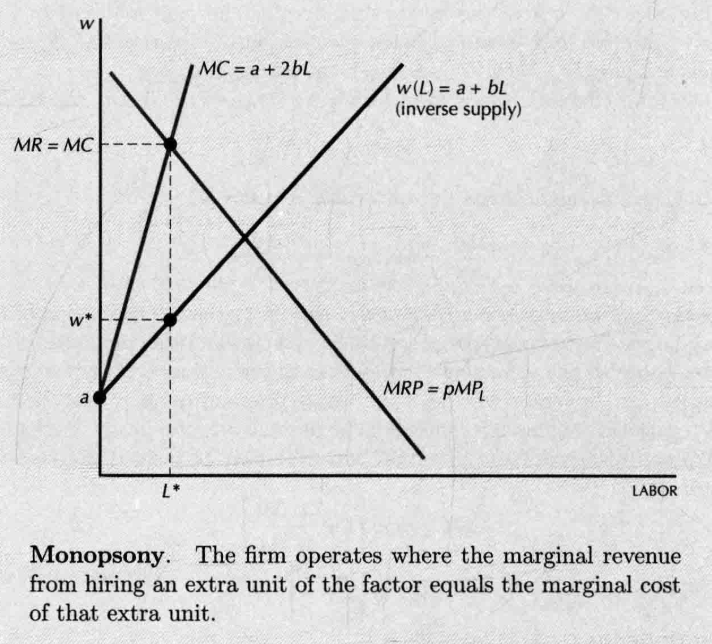
- Monoposony(买方垄断)
- 一个商品只有一个买主(也就是要素的购买者可以决定要素市场的价格)
- 竞争性要素市场上的厂商是价格接受者 price taker
- 买方垄断厂商是价格制定者 price maker
- 利润最大化问题:
- 边际收益
- 边际成本 , 是要素的供给弹性。若供给曲线无穷大,则与竞争性要素市场一致
- 相对竞争性要素市场而言,买方垄断厂商的要素使用量较少,这也是帕累托低效率的情况,它出现在要素市场。
- 一个商品只有一个买主(也就是要素的购买者可以决定要素市场的价格)
- Minimum Wage
- 竞争市场,政府规定的最低工资高于现行工资,这时劳动供给会超过劳动需求
- 若由买方垄断厂商支配,规定最低工资会增加就业量(比如等于竞争性市场上的均衡工资),这时它雇佣的公认数量与它面临竞争性劳动市场时雇用的工人数量相同
- 图片
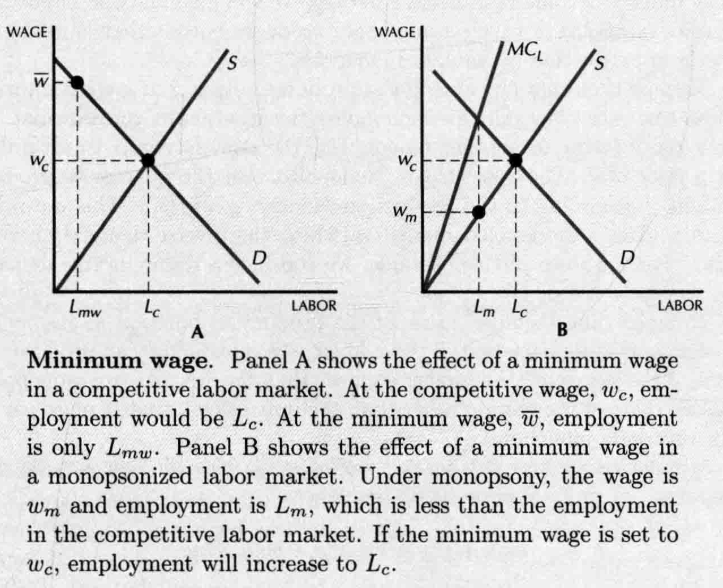
- 对买方垄断厂商规定工资下限,就如同对垄断厂商规定价格上限
- Upstream and Downstream Monopolies
- 考虑一家垄断厂商(upstream monoplies)的产品是另一家垄断厂商(downstream monoplies)的生产要素的情况
- 下游垄断厂商利��润最大化(假设 为反需求函数,生产函数为 ,必须支付给上游垄断厂商的单位价格 ):
- 边际收益等于边际成本
- 上游垄断厂商: ,设成本为 则
- 厂商的最终产量:
- 若这两个厂商合并成一个厂商,面临的产��品饭需求函数 ,边际成本为 ,则由 ,产量为
- 一体化垄断厂商的产量是非一体化垄断厂商产量的两倍(线性情况下的特例)
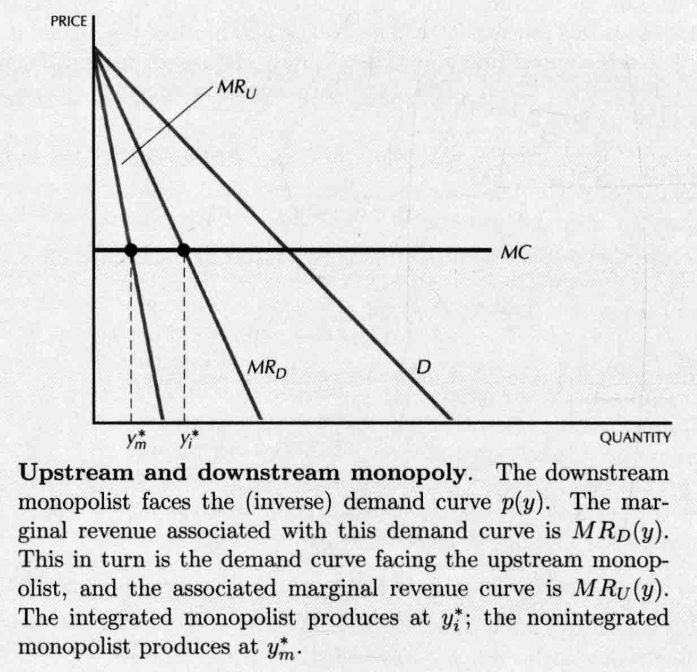
- 一体化垄断厂商总比上游-下游这对垄断厂商生产的更多。 在上游-下游这种情况下,由于经过了一次买-卖的中间环节,存在 double markup(双重加成定价),定价会很高,如果两个垄断厂商合并,价格就会下降,利润就会上升
Oligopoly
- 市场上存在许多竞争者,但没有多到每个竞争者对价格的影响忽略不计,称为寡头垄断(oligopoly)
- 关注行业中只有几家厂商的策略相互影响的问题
- duopoly(买方双头垄断),仅限于两家厂商,分析它们策略相互影响的情况。
- Strategy
- sequential game:
- price leadership: 一家厂商先决定价格(price leader),另一家也根据此做出选择(price follower)
- 均衡状态下,领导者和追随者的价格都是 ,这种情况类似于竞争模型,因为价格已经由领导者确定。
- 追随者利润最大化 ,令其等于边际成本,则得到追随者供给曲线
- 领导者可以出售的产量是 ,称为领导者的剩余需求曲线
- 领导者有不变的边际生产成本 但对于任意的价格 ,实现的利润是 ,之后直接选择边际收益和边际成本相等的价格和产量组合(对于剩余需求曲线)
- 均衡状态下,领导者和追随者的价格都是 ,这种情况类似于竞争模型,因为价格已经由领导者确定。
- quantity leadership: 先决定产量(quantity leader),另一家跟随决定(quantity follower)
- Stackelberg model, 领导者的产量是 ,追随者产量是 , 是行业产量 的均衡价格。领导者会��预期追随者在领导者的选择之下也实现利润最大化。
- 追随者的利润最大化 ,追随者把领导者的产量视为常量,追随者希望边际收益等于边际成本:
- 由于追随者的利润最大化产量受领导者的影响,故而 ,称之为 reaction function,设反需求函数 ,则追随者的利润函数 ,同时假设成本为 ,可根据 的不��同画出一堆等利润线
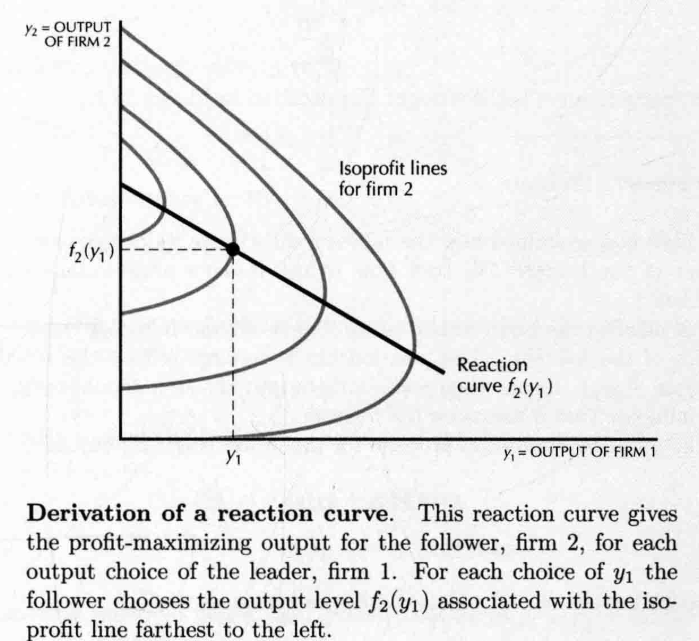
- 对于 的每一个选择, 要处在尽可能靠左的等利润线上(也就是等利润线的切线),这些切点汇合在一起,构成了追随者的反应曲线。
- 追随者的边际收益 ,令其等于 可以推出追随者的反应曲线
- 由于追随者的利润最大化产量受领导者的影响,故而 ,称之为 reaction function,设反需求函数 ,则追随者的利润函数 ,同时假设成本为 ,可根据 的不��同画出一堆等利润线
- 领导者的利润最大化问题: ,代入得 ,代入前面设定的反应函数/追随者的产量,领导者利润可以化简为 ,边际收益 ,令 , ,
- 追随者要沿反应曲线选择产量,所以领导者也需要在这条曲线上找利润最高的点,也就是找切线
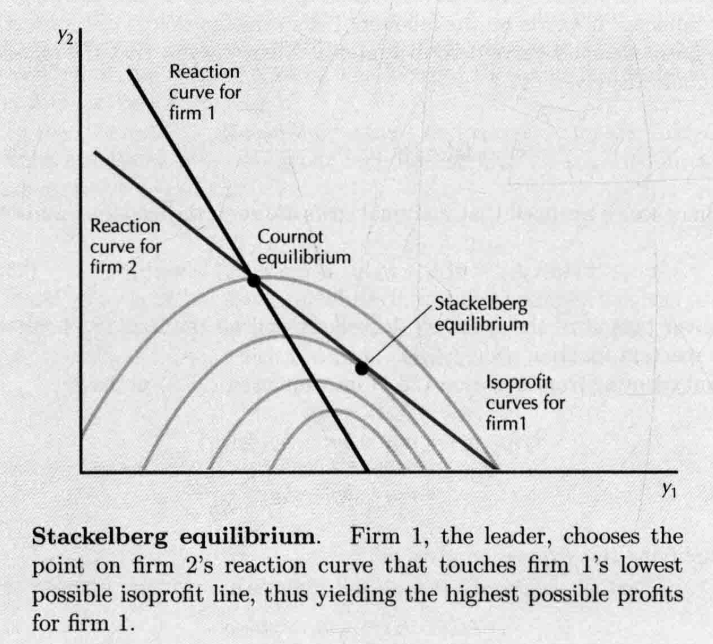
- 追随者要沿反应曲线选择产量,所以领导者也需要在这条曲线上找利润最高的点,也就是找切线
- 产量决定——厂商进行生产能力的选择
- 价格决定——厂商�分发价目表
- price leadership: 一家厂商先决定价格(price leader),另一家也根据此做出选择(price follower)
- simultaneous game,两家厂商不知道对方会做出什么决策,所以同时选择产量
- 选择价格
- 厂商为价格的制定者,市场决定销售的数量,称为(Bertrand competition)伯特兰竞争模型
- 若多家厂商销售的是同一产品,那么价格等于边际成本不变
- 选择产量
- 厂商1预测厂商2生产 单位产量,则总生产量 ,厂商1的利润最大化问题
- 反应函数:厂商1: ;厂商2:
- Cournot equilibrium: 古诺均衡,假设有产量组合 ,假设厂商2的产量是 ,厂商1的产量就是 ,反之亦然。
- 每家厂商的最优产量选择正是另一家厂商预期它会生产的产量,也就是反应曲线交点的产量,不断趋向于均衡点
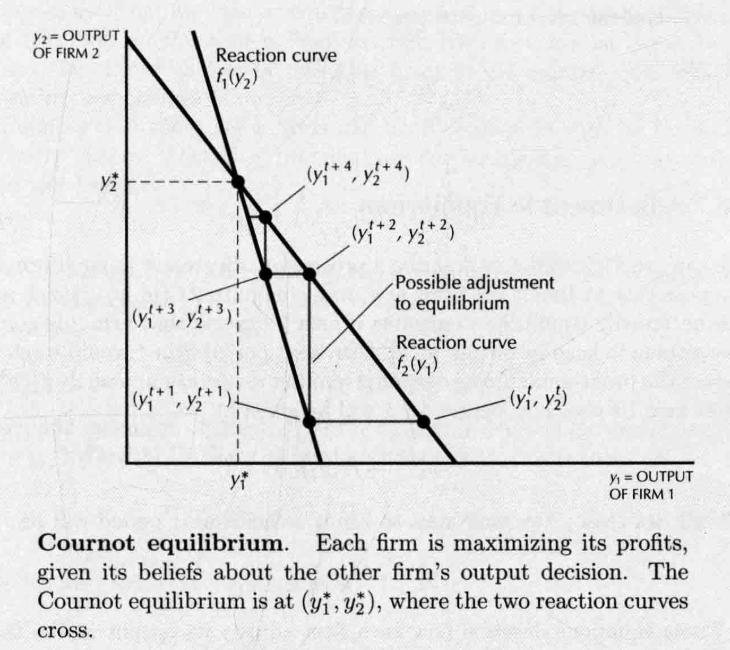
- 多家厂商的古诺平衡
- 家厂商, 为总产量
- 厂商 的边际收益等于边际成本的条件: ,其中 为厂商 在市场总产量中占有的份额
- 视为垄断厂商面临的需求曲线的弹性。
- 选择价格
- cooperative game: 厂商之间进行串谋(collude)
- 不同厂商串谋,追求它们利润总和的最大化:
- 最优条件 也就是每家厂商的等利润线必然相切。
- 但是串谋的厂商们总是受到作弊的诱惑: (等号右侧的原因:市场需求曲线的斜率为负值),最后有 ,也就是只要厂商1认为其他厂商的产量保持不变,就可以增加自己的产量来获取利润。
- 零边际成本和线性需求曲线下的卡特尔解:
- 总利润函数
- 用边际成本为 的条件:
- 等利润线的公切点便是卡特尔解,是一个不稳定的解
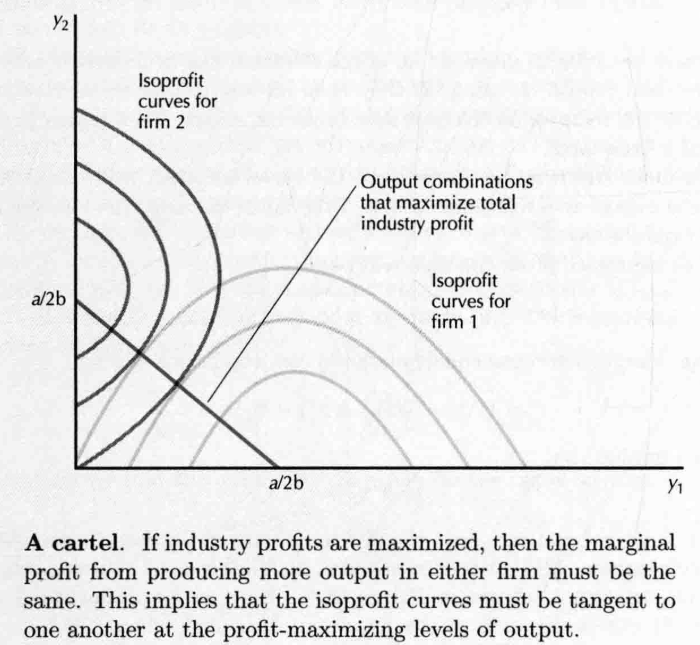
- Punishment Strategies:若出现欺骗行为 生产古诺产量作为惩罚。
- 设卡特尔利润 ,偏离限额利润 ,古诺利润
- present value of cartel behavior
- present value of cheating
- 时,厂商维持卡特尔产量时的value高于违反时的
- 只要利率足够小,限额生产就值得,但仍然有不足:因为惩罚需要一定的时间。其他模型会更多地考虑短时期内的惩罚。
- 另一些惩罚措施:向消费者保证一旦另一家厂商降价,自己也降价
- sequential game:
- price matching: 提供低价保证的供应商剥夺了大多数竞争对手的降价动机
- 比较:
- 串谋的产量最小,价格最高
- 伯特兰均衡(竞争均衡)的产量最高,价格最低
Game Theory
- general analysis of strategic interaction
- use payoff matrix
- dominant strategy:
- 不论其他人如何选择,每个参与人都有一个最优策略
- 若博弈中每个参与人都有一个占优策略,那么这个组合就是博弈的最后均衡结果
- Nash Equilibrium
- 在 的选择最优的条件下(进行 的选择),选择的结果与 的选择最优的情况下(进行 的选择)相同
- 是古诺均衡的一般化形式
- 一个博弈可能会存在一个以上的纳什均衡,而且有的博弈根本不存在纳什均��衡
- 纳什均衡不一定会导致帕累托有效率的结果——the prisoner's dilemma
- (deny,deny)is pareto efficient while (confess,confess)is not only a Nash equilibrium, but also a dominant strategy equilibrium
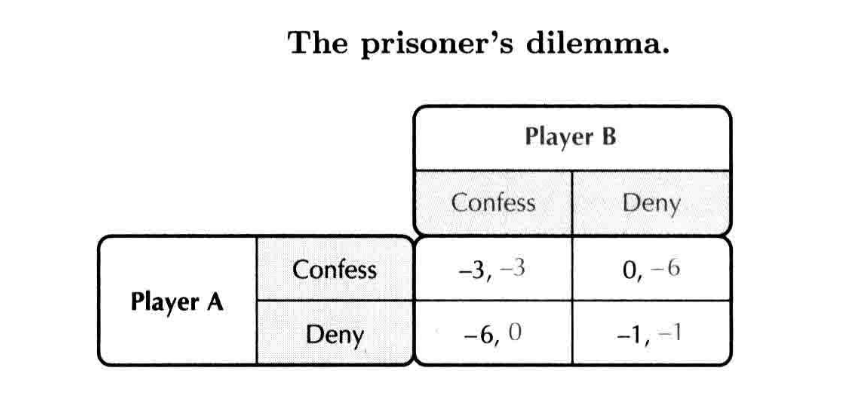
- 到底该做出怎样的选择,取决于进行一次性博弈还是无限次重复博弈
- (deny,deny)is pareto efficient while (confess,confess)is not only a Nash equilibrium, but also a dominant strategy equilibrium
- pure strategy: 每个参与人只选择一种策略并始终坚持这个选择
- Mixed Strategies: 给每个选择指定一个概率,并按照概率选择策略
- repeated games
- fixed number of times
- 局数固定且已知的博弈中,合作解取决于最后一句的策略
- indefinite number of times
- 总收益最高的策略是“针锋相对”(tit-for-tat)
- 卖方双头垄断的定价策略博弈与囚徒困境有相同结构的收益矩阵
- 但这种博弈如果重复无限次,且每个参与人都知道对方采用的是“针锋相对”的策略,就会担心因自己的降价而触发价格战
- 持续一段时间的低价可能是为了发出竞争的信号而非争夺更大的市场份额
- fixed number of times
- Sequential Games
- 当博弈的顺序确定时,若博弈中出现好几个均衡,有的均衡可以被“顺序”排除掉。
- game of entry deterrence
- 假设有新进入垄断市场的进入者,且垄断市场中的在位者购买了额外的生产能力,可以与新进入垄断市场的进入者斗争
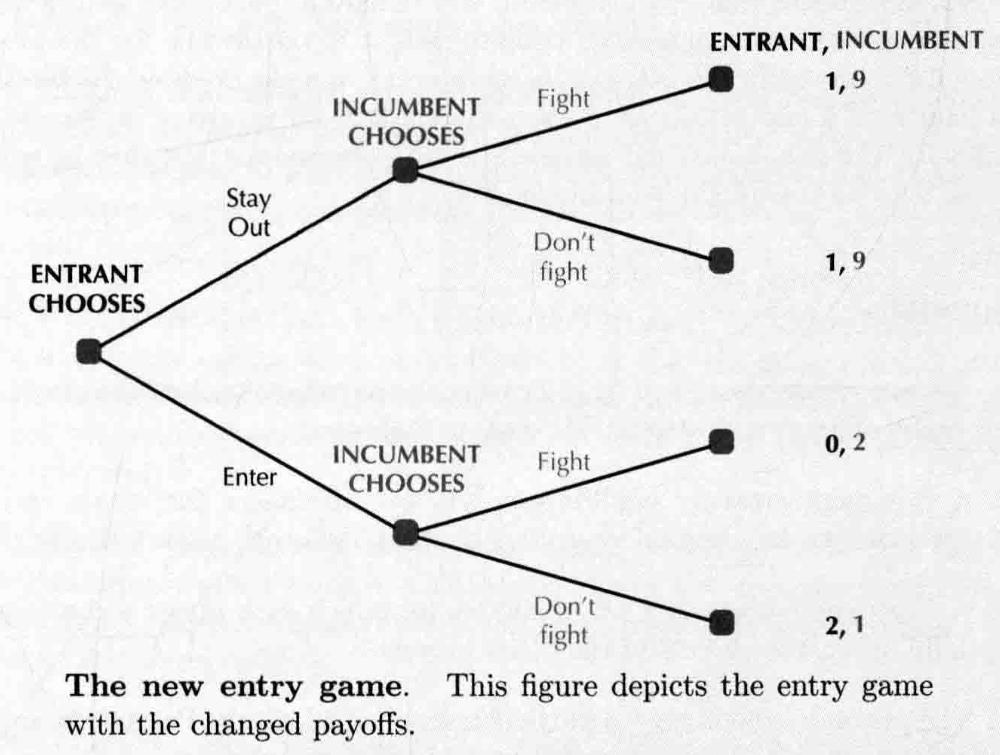
- 在位者为了维持现有的垄断地位,会努力投资额外的生产能力,却永远不会�利用额外的生产能力。
- 假设有新进入垄断市场的进入者,且垄断市场中的在位者购买了额外的生产能力,可以与新进入垄断市场的进入者斗争
- Best Response Curves
- 设行参与人 ,对行参与人的选择,列参与人的最优反应: ,列参与人 ,行参与人的最优反应
- 再定义:纳什均衡是一个策略组合 , ,
- 参与人可能在几个最优反应之间无差异,所以 是列参与人的最优反应之一, 是行参与人的最优反应之一
- 计算最优反应曲线,以及 mixed strategies
- 设定参与人的选择概率,并且根据组合计算出概率和收益
- 假设某个选择增加了 ,分析收益的变化
- 绘制最优反应曲线,最后得到纳什均衡(交点)
- 示例
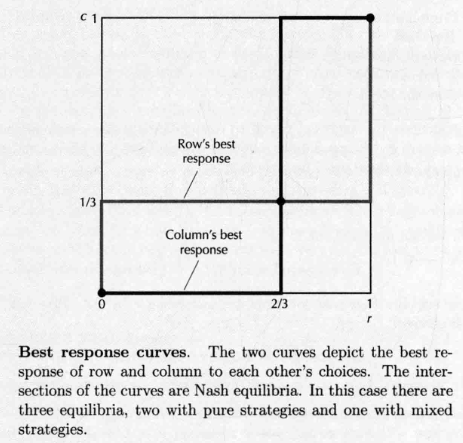
simultaneous moves
- coordination games:当参与人能够协调他们之间的策略时,他们的收益就会实现最大化
- 但需要创建一种能够实现这种协调的机制
- 若某个均衡相对其他均衡更“自然”时,均衡称为博弈的 focal point
- 例子
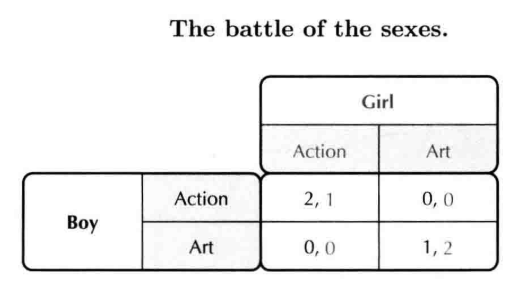
- battle of sexes 在其中一方偏爱的均衡处合作
- 囚徒困境 增加博弈的次数/增加缔结合约的可能性
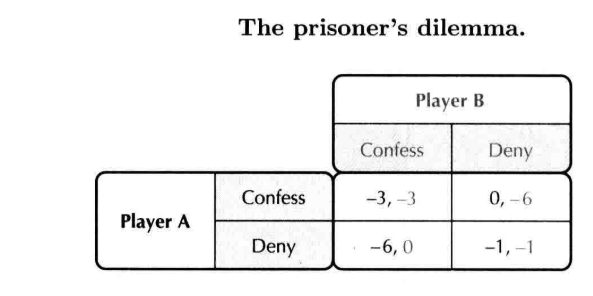
- assurance game: 与做不同的事情相比,博弈双方做相同的事情时的境况较好 在双方都偏爱的均衡出合作
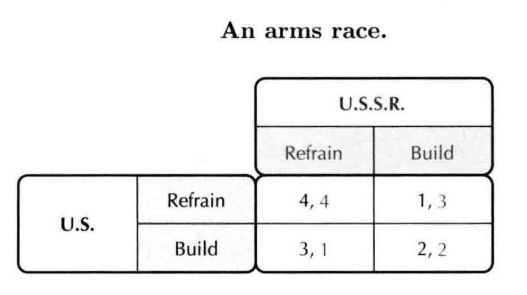
- Chicken 做出某种承诺/选择实现你偏爱的结果
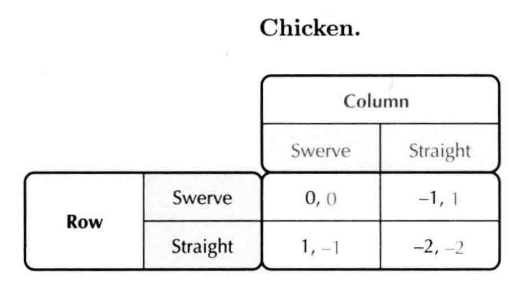
- battle of sexes 在其中一方偏爱的均衡处合作
- Games of competition/zero-sum games: 一方的收益等于另一方的损失
- 需要找到均衡策略(equilibrium strategies),使得不管对方采取什么行动,都能得到相等的收益。
- Games of coexistence
- 从博弈论的角度看动物行为问题
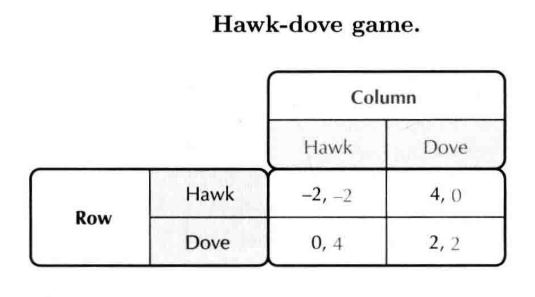
- 可以假设鹰派的比例是 ,鸽派的概率是 ,计算出二者的期望收益,当某个种群的期望高于另一种群,对应种群的数量就会上升。种群处于均衡状态:两种类型的收益相等
- 可以通过上述分析看它是否是一个在进化动力下稳定的均衡(evolutionarily stable strategy), 一个ESS就是一个纳什均衡
- 从博弈论的角度看动物行为问题
- sequential moves
- Games of commitment
- 如果其中一方先采取行动(承诺),结果就会更有利
- 被承诺的选择必��须同时是不可撤销的和可观察的
- 如果想改变博弈的结果,就要想办法做出可以导向那个结果的保证
- bargaining
- nash bargining model
- rubinstein bargining model
- 在三天内协商分配问题,第一天 提出报价,第二天 接受 / 拒绝这个报价(同时提出新报价),第三天 提出最后的报价,若不达成协议,双方都会一无所获
- 若 和 的 discounts payoffs in the future 都是 ,那么有
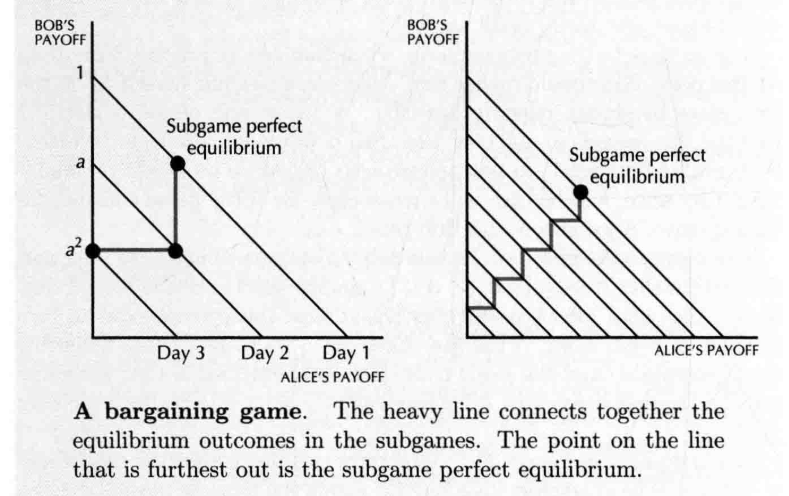
- 无限博弈:
- 有 将来收益的贴现因子的
- :
- Games of commitment
Exchange
- partial equilibrium: 探求需求与供给条件如何受特定商品的影响
- general equilibrium: 几个市场的需求与��供给条件如何互相影响,决定多种价格,但比较复杂,做如下简化
- 竞争市场
- 两个商品和两种消费者
- 先考察纯交换(pure exchange,不考虑生产),再考虑生产行为
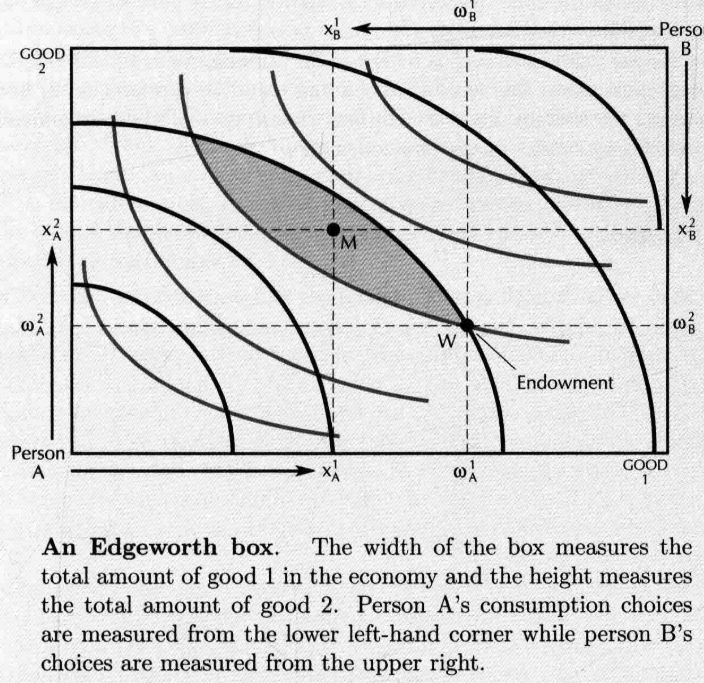
- Edgeworth Box:表示两个人之间两种商品的交换
- 行为人 / , 的消费束 , 的消费束 ,若消费商品的总数与禀赋量相同,则配置是可行配置( ,初始禀赋配置(initial endowment allocation) , 同理)
- 在交换商品之中最后达到最终配置 (final allocation)
- 向右上移动,移向 更好的配置,向左下移动,移向 更好的位置
- Trade: / 无差异曲线之上的部分可以让二者都变得更好。可以通过互利交易进行趋向阴影部分中任何一个点的移动。之后再在这个点上再画无差异曲线再移动…… Pareto Efficient Allocations(无差异曲线相切)
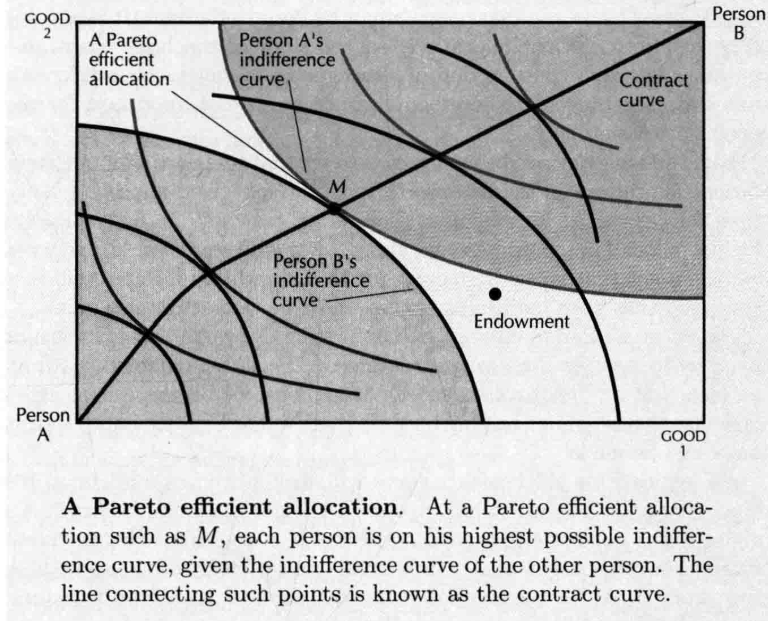
- 上图中存在许多Pareto efficient allocations,给定 的任一一条无差异曲线,就可以找到一个这样的点(相切即可),这些点的集合称为 Pareto set 或者 contract curve(任何交易的最终契约必定在帕累托集上)
- Pareto efficient allocation
- 无法使任何一方境况更好
- 不可能使一方境况更好,又不使另一方境况变坏
- 从交易中能得到的所有收益都取尽
- 无法进一步做互利的交易
- 帕累托集描述了任何一点开始的互利交易的全部结果,除了初始禀赋 两种商品的总数 Edgeworth Box 大小之外,帕累托集本身不取决于初始商品禀赋(而是取决于无差异曲线)
- Market Trade (对该问题进行更精准的描述,模拟一个竞争市场结果的交易过程,这里 和 不只是一个人而是一类人。)
- 设第三者,充当“拍卖商”的角色,选定商品价格 ,之后 , 进行商品选择:
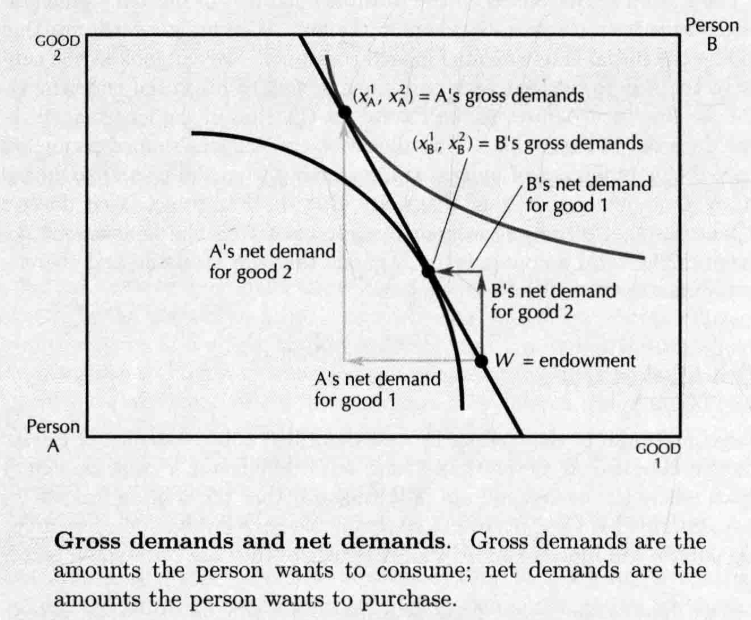
- 但是可以看到,这里 和 的供给和需求并不匹配,市场不会出清,处于 disequilibrium 状态,这个时候,拍卖商就会调整价格直到供求相等。
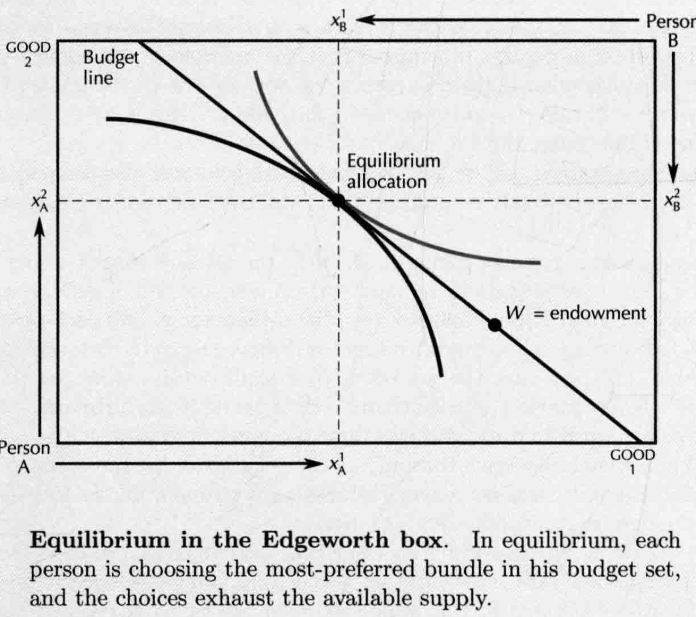
- 达到 equilibrium/market equilibrium/competitve equilibrium/Walrasian equilibrium
- 此时所有消费者的两种商品之间的边际替代率相同,无差异曲线相切
- 所有市场均衡都是帕累托有效率的(可以通过假设存在其他可行的配置求出),这称为 First Theorem of Welfare Economics
- 这东西的假设:
- 消费者只关心本人的商品消费,而不关心他人的(没有 consumption externality)
- 每个消费者确实在竞争
- 竞争均衡确实存在(消费者的消费量相对市场规模充分小)
- 竞争市场的特定结构可能有助于实现帕累托有效性(在配置资源方面)
- 这东西的假设:
- 设第三者,充当“拍卖商”的角色,选定商品价格 ,之后 , 进行商品选择:
- algebra of equilibrium(描述均衡)
- 需求与供给量相等
-
- 左侧第一项可表示为 ,同理另一项可表示为 ,称为对应商品的净需求(net demand)/超额需求(excess demand)
- 若把这两项的加和用(在这里是对商品1的)总超额需求(aggregate excess demand)表示为
-
- 用总超额需求表示这种均衡状态 ,也就是
- 通过 Walras' law 了解总超额需求函数的特性
- (由于每个消费者的超额需求等于 则所有消费者的总超额需求等于
- 由这个式子我们知道: 有 种商品的市场,只需找到一组使 种商品的市场处于均衡的价格,这样可以保证商品 的市场中需求与供给自动相等。
- 只有 种独立价格
- 由于
- 需求与供给量相等
- 均衡的存在性(existence of a competitive equilibrium):关键假设,总需求函数是连续的
- 每个人的需求函数需要是连续函数(消费者有凸状的偏好)
- 消费者的人数小于市场规模(与竞争行为的假设相符:消费者数量很多,但与市场规模相比又很少)
- Monopoly in the Edgeworth Box
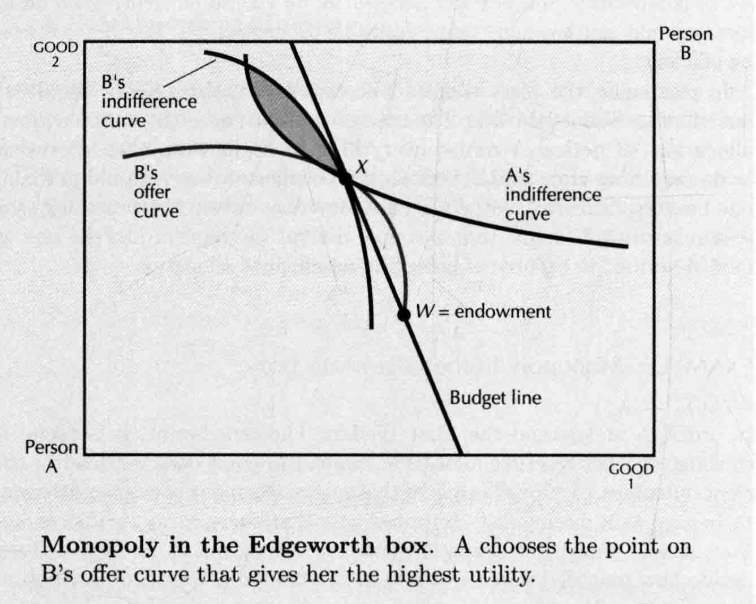
- 普通垄断者: 向 报价, 按照 的报价确定成交量。选择点是 的提供曲线与 的无差异曲线的切点,从这点画直线到商品禀赋 点,可以获得对应价格。但这点并非帕累托有效率点。
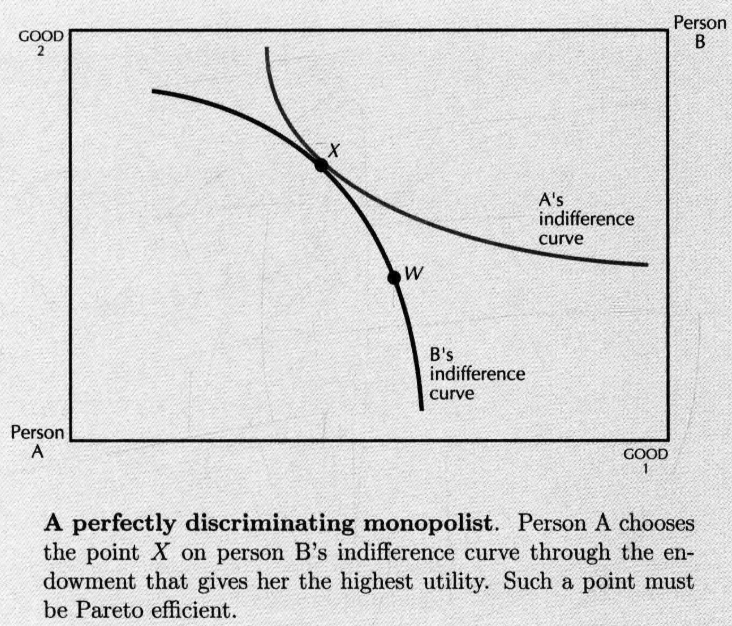
- 完全价格歧视者: 按不同的价格向 出售对应商品,最终到达切点。这个点是帕累托有效率的。
- 普通垄断者: 向 报价, 按照 的报价确定成交量。选择点是 的提供曲线与 的无差异曲线的切点,从这点画直线到商品禀赋 点,可以获得对应价格。但这点并非帕累托有效率点。
- 是否存在帕累托有效率配置,可以找到使市场均衡的价格?
- 这与 , 是否呈凸性相关。
- 呈凸性,切线即为预算线,交易者选择预算集上的最佳消费束,均衡即为初始帕累托有效率配置
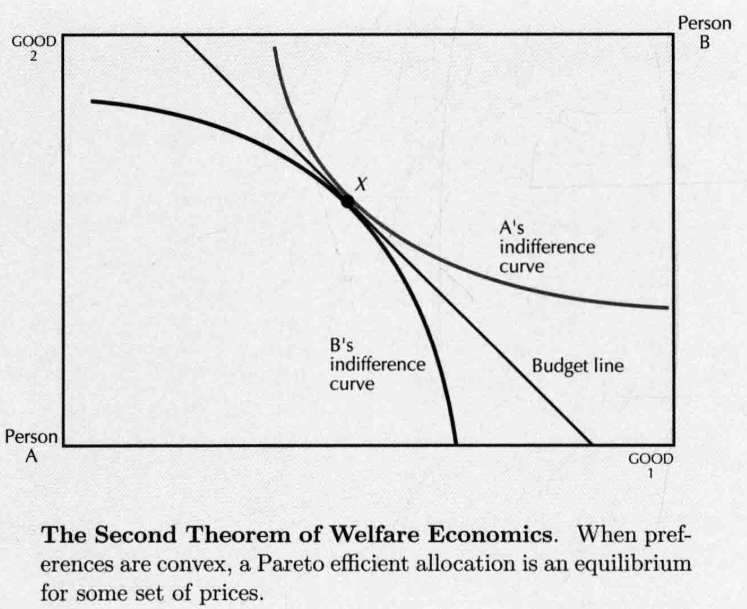
- 不呈凸性,最可能的预算线上 和 的最佳需求不一致( 是 , 是 )
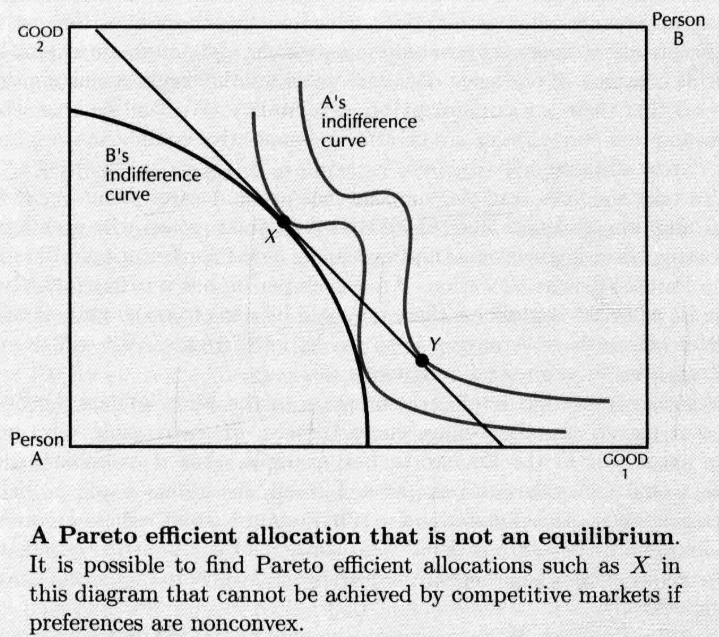
- Second Theorem of Welfare Economics: 如果所有交易者的偏好都是凸型,则总有一组价格,每一个帕累托有效率配置都是在适当商品禀赋条件先的市场均衡
- 分配和效率问题可以分开讨论(任何帕累托有效率配置都能得到市场机制的支持)
- 价格的双重作用
- 配置,表明商品的相对稀缺性
- 分配,确定不同的消费者能购买的商品数量(可通过重新分配商品禀赋来确定)
- 国家可以通过转移禀赋的购买力(比如按照消费者禀赋的价值征税,把钱转移给他人)来解决分配问题,这时候仍然能带来帕累托有效率配置。(但是按照消费者的选择征税时,会导致无效率的结果,因为税收会影响边际选择,也就影响了配置)
- 但是测定人们的禀赋是很麻烦的,若禀赋的主体是劳动力,人们的劳动禀赋就是其考虑出卖的劳动而不是实际出卖的劳动(若按实际出卖的劳动出卖,就是一种扭曲税(distortionary tax) ),这带来了一些困难
- 呈凸性,切线即为预算线,交易者选择预算集上的最佳消费束,均衡即为初始帕累托有效率配置
- 这与 , 是否呈凸性相关。
Externalities
- Consumption externality: 消费者关注另一个经济行为人的生产或消费
- Production externality: 厂商的生产可能会受到另一个厂商或者消费者选择影响的时候
- 特征:存在人们关注但又不在市场上出售的商品
- 外部效应出现,市场就不一定能产生资源的帕累托有效应供给,而法律体系和政府干预可以一定程度地模拟市场,从而实现帕累托有效率
- Consumption externality: 假设在下图中,抽烟对 来说有益,对 来说有害,那么我们仅用从左下角沿纵轴度量全部的烟量。
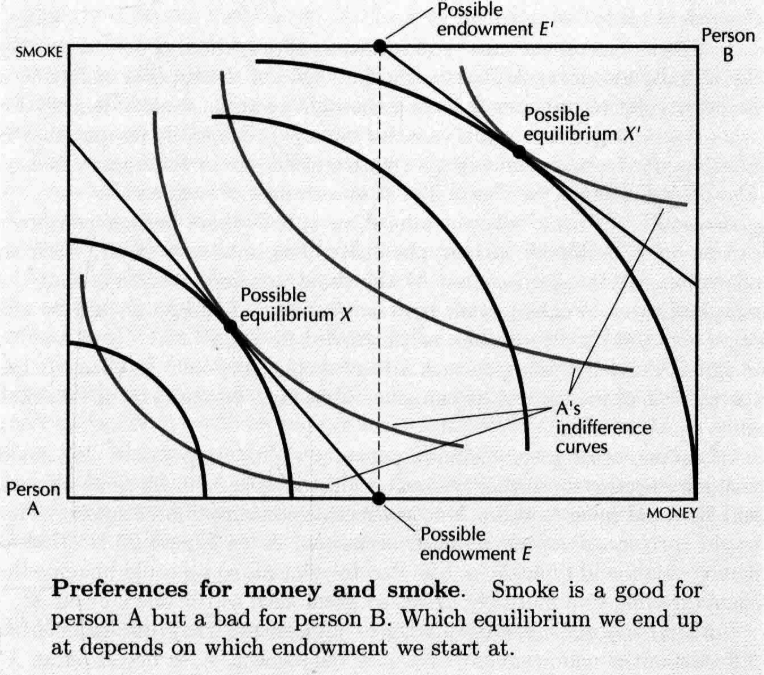
- 点: 拥有洁净空气的法定权利 是帕累托有效率配置点
- 点: 可以随心所欲的抽烟 是帕累托有效率配置点
- 唯一的不同是:需要界定涉及外部效应的商品的产权,但问题在于有时产权难以界定。
- 但如果行为人的无差异曲线是拟线性的,那么每个有效解都会有相同数量的外部效应
- Coase Theorem: 涉及外部效应的商品的有效率数量独立于产权分配
- Production Externalities
- 生产钢 ,同时产生污染物 ,成本函数 ,污染使得钢的生产成本减小 ; 生产鱼 ,成本函数 ,污染使得鱼的生产成本增加
- 的利润最大化问题 (可以选择产生污染物的数量)(私人成本 private cost 最小化)
- 条件 , (假定污染的价格为 )
- 的利润最大化问题 (必须接受污染物的水平)
- 条件 (随污染增加而增加的渔场的成本是生产钢的社会成本(social cost),钢厂对这种成本是忽略不计的)
- 但如果把两个厂合并成一个厂,这个厂就必须考虑生产污染物的成本——外部效应被内部化(internalized)了——这也是社会成本(social costs)最小化的条件
- 合体企业的利润最大化问题
- 条件: , ,
- 最后一个条件表明,这个合体企业需要考虑污染量。这个条件可以转化成 (都是对 的偏导)由于污染的增加会带来成本的增加,故而 大于 ,于是 必然小于 ,因而比独立的钢厂排放较少的污染物。
- 如果私人成本和社会成本分开,单靠市场就可能不足以实现帕累托效率。
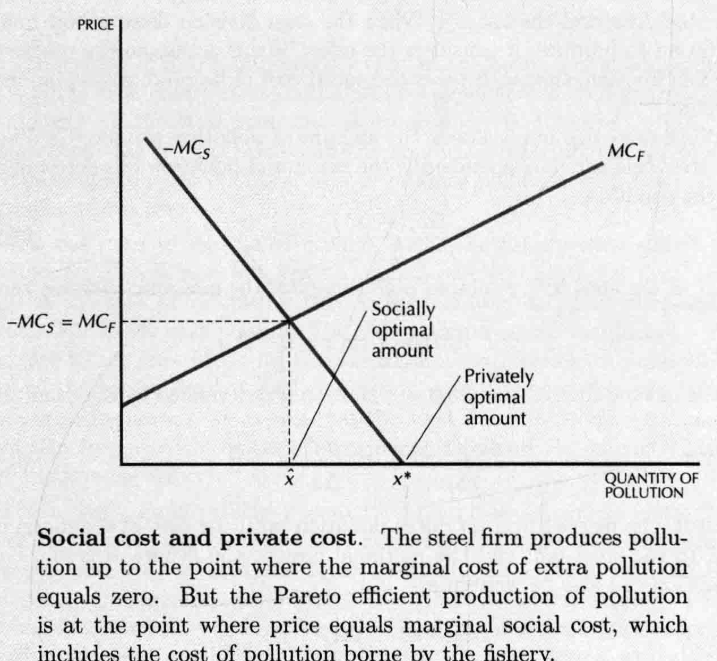
- 纠正外部效应
- 钢厂面临不正确的污染价格 对钢厂排放的每单位污染征收 美元的税金
- 利润最大化问题:
- 利润最大化条件
- 若 ,则上述条件等同于帕累托有效率污染水平的那些条件,这种税称为 Pigouvian tax,为了征收这种税,我们需要知道最适合的污染水平。
- 不存在污染物市场 假设消费者可以出售清洁环境的权利,设每单位污染为
- 利润最大化问题:
- 钢厂:
- 渔场:
- 利润最大化条件
- 也即
- 如果让钢厂有权排放污染,而渔场购买产权,也会得到有效率的结果
- 利润最大化问题:
- 这两个企业不��合并是不是有点儿问题 市场信号(Market Signals):市场本身提供了使外部效应内部化的信号。
- 钢厂面临不正确的污染价格 对钢厂排放的每单位污染征收 美元的税金
- 产权不明确带来的问题:
- 两种配置机制( 是牛的数目, 是一头牛的成本, 是牛生产的价值
- 私��人所有一块地,并且放牛
- 最大化问题
- 最优产量:
- 这块地由很多人共同所有
- 对于放牧的每个人,最优产量是平均产量等于边际成本之时:
- 跟上面最优产量不同的原因是,一个人拥有的牛的数量相对于牛的总数忽略不计。
- 私��人所有一块地,并且放牛
- 多人共同使用会造成外部效应,或者说这其中的每个个体都忽略了增加放牧的 social cost
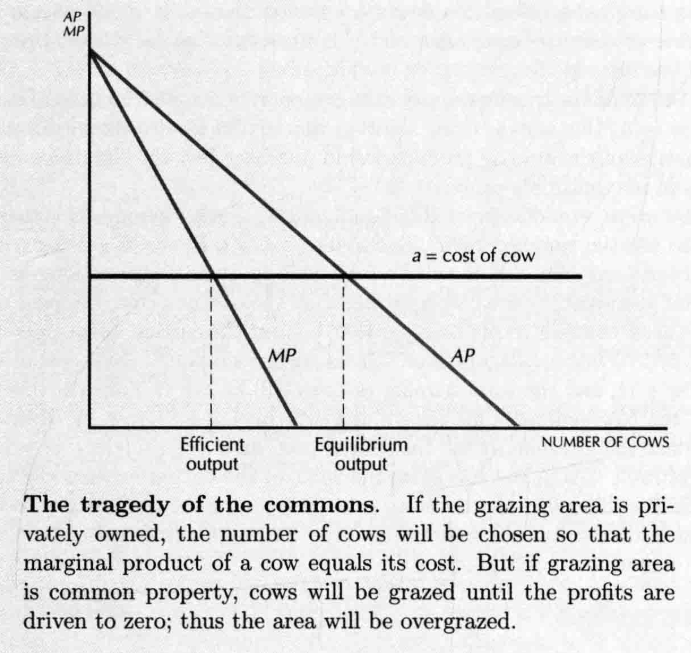
- 私人产权在一些情况下可以消除外部效应,因此带来帕累托有效率的结果,虽然它不是促使资源有效使用的唯一社会制度,用法律大概也可以,但法律不明确的时候,就会导致资源无法得到有效使用。
- 两种配置机制( 是牛的数目, 是一头牛的成本, 是牛生产的价值
Public Goods
- Public goods: 对所有涉及的消费者都必须供应同样数量的物品
- 例子:俩人买公共电视机
- 最初的财富, 对购买电视机所做的贡献, 是剩余下来用做私人消费的�资金
- 保留价格(reservation price) 使行为人觉得支付 的价格购买某物品与根本不购买这两种选择之间毫无区别。
- 购买电视机的条件:
- 更多的私人消费必然增加效用
- 购买电视机成为帕累托改进的充分条件
- 是否提供公共物品取决于人们的支付意愿和公共物品的总成本
- 提供公共产品是否是有效率的,取��决于初始的财富分配 保留价格 etc
- 公共物品与财富分配无关的情况:两人的偏好是拟线性的
- 保留价格 ,
- 在一定范围内( , )公共物品的最优供给与财富无关
- 公共物品与财富分配无关的情况:两人的偏好是拟线性的
- 有可能出现“搭便车”的现象,即每个人都不如实地表明对公共物品的评价,期望另一个会独立购买公共物品
- Free Riding
- 假设电视机成本150,每个人愿意支付100,则有博弈矩阵
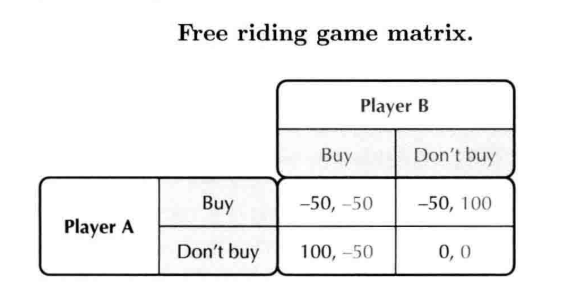
- 占优策略:没人购买电视机
- 最大化总体效用的策略:一个人买,双方都看
- 帕累托改进:一个人买,但另一个人给买电视机的人一笔钱(超过成本)
- 但人更多的时候,就更麻烦,会有更多人想要“搭便车”
- 用最大化问题和均衡进行分析
- 第 个人的效用函数 , ,
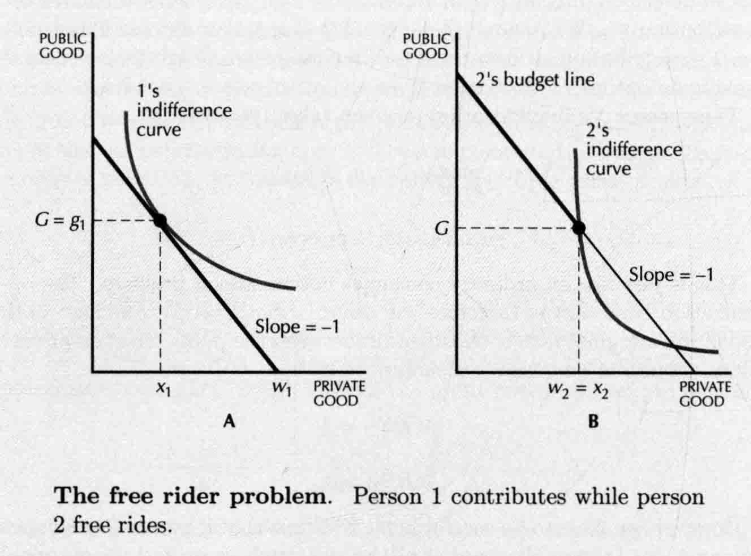
- 行为人1假定行为人2购买了一定量的公共物品
- 行为人1的最大化问题: ,但也有可能行为人2觉得行为人1贡献的公共物品的数量完全够用,于是就决定搭便车。
- 图 中行为人2的预算线只有上半截是有效的,因为2不可能减少公共物品的数量
- 假设电视机成本150,每个人愿意支付100,则有博弈矩阵
- Different levels of the public good
- 代表公共物品的质量, 代表对应的成本
- 约束条件:
- 帕累托有效率
- 最优化条件 (对公共物品的边际支付意愿相加之和超过边际成本)
- 对应的条件:
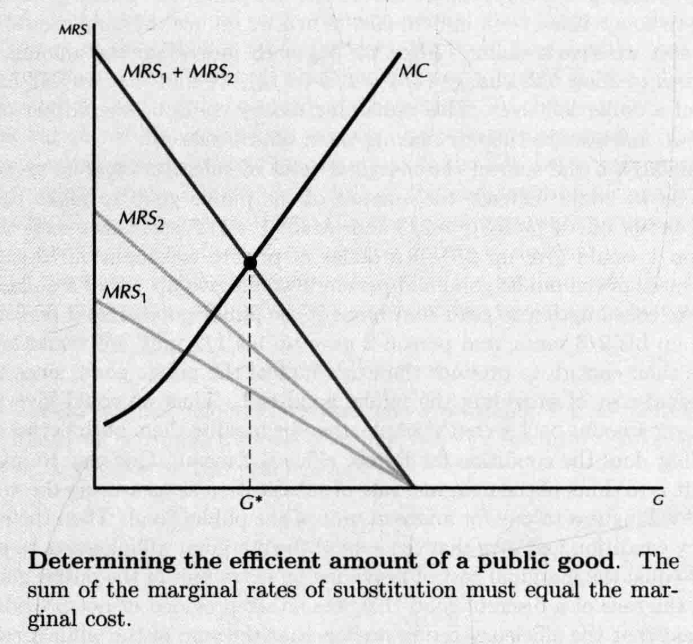
- 代表公共物品的质量, 代表对应的成本
- 若消费者具有拟线性偏好:
- 则前述公共物品的帕累托有效率水平为 ,这跟 无关 存在一个唯一的公共物品有效供给数量
- 拟线性偏好条件下:固定公共物品的数量,只要重新配置私人物品就可以得到所有帕累托有效率配置形式
- 市场提供的公共物品不太可能导致帕累托有效率提供量。
- command mechanism: 由一个人或一小部分人决定公共物品的数量
- voting system
- 阿罗不可能定理 所有的社会偏好顺序可能是一个人的偏好排序
- 即使人们有 Single-peaked(单峰)偏好(不满足阿罗不可能定理),选择的支出水平(也即中位数支出水平(median expenditure))并不是有效率的数量水平(因为这仅仅反映了一半的人要增加开支,另一部分人要减小开支,并没有涉及到他们需要的公共物品的数量)
- 一系列投票的结果可能取决于投票的顺序
- The Vickrey-Clarke-Groves Mechanism
- 确定行为人的效用函数
- Groves mechanism
- 每个行为人报告愿意为提供 单位公共物品承担的费用
- 选择最大化报告效用总和 的公共物品数量
- 每个行为人收到一个 sidepayment,具体表示为
- 分析
- 行为人的总收益: ,且行为人意识到决策者将用自己报告的效用函数最大化效用总和 ,所以他最后会报告自己的真实效用
- 在不同行为人之间“内生化外部性”每个行为人承担自己的报告给其他人带来的成本和收益
- 但是 sidepayment 是很大的一笔钱
- Vickrey-Clarke-Groves Mechanism
- 可以向行为人征税,只要税收独立于行为人的选择就可以
- 向行为人 征收税额等于除行为人 之外的其他人报告的效用综合最大值
- 减去之前的 sidepayment,净税额等于 (在这里,后者是所有人效用最大值时行为人之外其他人的效用,必然小于 个人时效用的最大值)
- 解决买电视中的搭便车问题
- 是行为人对电视的估价
- 行为人 的收益:
- 最后一项与行为人 无关,所以仅仅考虑前两项:
- 若上式为正, 即可购买电视
- 若上式为负,只要报告 就不会买
- 只有行为人改变社会决策(改变最终的支付结构/资源分配)时,才必须上交“税额”(相当于他对其他人施加的成本),这时该行为人是 pivotal 的。
- 问题
- 仅适用于拟线性偏好,因为这时行为人偏好的公共物品的数量不受行为人为其支付的费用多少的影响
- 不能带来帕累托有效的结果,因为上面提到的“税额”会影响行为人的私人消费
- 串谋会影响VCG机制
- VCG机制确保了若每个人因为提供了公共物品而境遇会变得更好时,就会提供公共物品;并不意味着实际提供公共物品时,每个人的境遇实际上�会变得更好,因为它只说明存在一种支付计划,使得那种帕累托有效 每个人境遇会更好的情况可能存在,实际的支付计划不一定是那个最好的
- 不存在这种理想的支付计划:它既可以决定是否提供公共物品,也可以决定分担费用的帕累托有效率方式。
Asymmetric Information
- 考虑信息不对等给市场带来的问题
- Quality Choice
- 由于获得信息的高成本,低质量的商品挤出高质量的商品
- eg:保险公司应该将费率建立在其潜在购买者的基础上而非平均购买者的基础上,因为想要购买保险的那部分人担心的事情总是更可能发生(因为逆向选择)
- 每个人的境况会由于强制要求购买反映全体居民平均风险的保险而变得更好(高风险群体的费用降低了,低风险群体可以以更低的价格(比只有高风险人群买保险时的价格更低)买到保险)
- 因此出现了国家/公司将保险作为福利的例子
- Adverse Selection
- 市场的一方不能查知市场另一方商品的“类型”/质量,称为 hidden information
- 如果一个市场中充满“俏货”和“次货”,二者的价格不同,但潜在的消费者并不知道商品��的好坏,所以就只能对商品的价格进行猜测。考虑到“俏货”和“次货”的比例,消费者的预期价格应该在二者价格之间的某个位置。但是在这个位置,只有“次货”的售卖者愿意售卖物品。消费者如果想到这一层,就会再度压低自己的出价。
- “俏货”和“次货”之间存在外部效应,“次货”卖家出售“次货”的行为让购买者对市场上货品的平均质量产生了“低质”的预期。
- 假设生产者可以决定售出商品是“俏货”还是“次货”
- 二者的成本相等,但消费者愿意为它们付款的数量不同(一个低于成本,一个高于成本),因此可以分类讨论
- 只生产“俏货”,因为竞争,售价会等于成本,但消费者原本愿意为它付款更多,所以有消费者剩余
- 只生产“次货”,售价等于成本,但消费者不愿意以成本价购入,所以卖不出去一点
- 两个都生产,设“俏货”的比例是 ,则需要满足
- 二者的成本相等,但消费者愿意为它们付款的数量不同(一个低于成本,一个高于成本),因此可以分类讨论
- 如果生产者能调配“俏货”/“次货”的比例(这时二者的成本不同)
- 由于“次货”成本更低,在竞争市场更占优势,所以大家都开始生产“次货”
- 如果消费者愿意付给“次货”的价钱低于“次货”的成本,那么生产者就寄了,卖不出去一点
- 破坏了两种商品的市场
- 相对于具有充分信息的均衡而言,这种均衡总是低效率的。
- 但是与此同时,拥有“俏货”的生产者会向消费者传递 signal ,比如说 warranty(保证书)
- 有时会使市场运行得更好
- 另一些情况下,会使市场运行得更差
- separating equilibrium: each type of worker making a choice that allows him to separate himself from the other type
- 低效率的。假设劳动力市场上有能干的人和不能干的人,且这两种人的生产率不会因为受教育高低而变化,能干的人还是会付出受教育的成本,因为这发出了信号,让用人单位愿意以更高的工资雇佣他。
- 有个人效益但没有社会效益。
- sheepskin effect: 同样相差一年的教育经历,在一年后获得文凭的人会比没有文凭而仅仅是读了一年书的人的工资更高。
- polling equilibrium: each type of worker makes the same choice
- separating equilibrium: each type of worker making a choice that allows him to separate himself from the other type
- Moral Hazard: 人们由于买了保险,知道坏事发生时也有保障,于是不去进行让坏事概率降低的行动(称为提防行动, or taking care)
- 源于市场的一方不能查知另一方的行动的情形,有时被称为 hidden action
- 保险公司�会把费率建立在提防行动的量的基础上,但问题是保险公司不能知道消费者所有的行动
- 如果保险公司不能查知提防行动的水平,它是不会允许消费者购买他想要购买的那么多的保险的。
- Incentive
- 工人付出的劳动, 产量(设价格为1,这也成为价格的测度), 报酬, 劳动成本
- 工人的效用:
- 让工人愿意参加工作,需要让工人在工作中获得的效用至少等于在别处他获得的效用
- participation constraint: ,最好是刚刚满足条件。
- 让工人愿意参加工作,需要让工人在工作中获得的效用至少等于在别处他获得的效用
- 老板的利润:
- 利润最大化: ,代入工人的条件:
- 求解 ,获得了老板想让工人工作的劳动量
- 的设计思路:让工人工作 的效用大于其他时候的效用,也即 (incentive compatibility constraint)
- 工人的效用:
- Incentive scheme
- optimal
- Rent: ,其中 是 rent
- 工人追求的最大化: ,最大化的结果恰好满足
- 同时要满足participation constraint
- Wage labor: , 是每单位劳动的不变工资, 是一次性总付的报酬
- 当 时,满足最大化达到
- Take-it-or-leave-it: 只有工作量为 时,才能得到报酬 ,否则啥都没有
- 由于participation constraint
- Rent: ,其中 是 rent
- nonopotimal
- Sharecropping: 工人和土地所有者每一方都按照固定的百分比从中收获, ,其中
- 工人的最大化问题 ,最大化时 ,不满足条件
- Sharecropping: 工人和土地所有者每一方都按照固定的百分比从中收获, ,其中
- 须保证进行劳动量决策的个人是产量的 residual claimant (剩余索取者)
- 激励计划向工人提供的边际效益等于他的边际产品。
- optimal
- 但上面的分析十分理想,实际情况并非如此,这是因为厂商的所有者很难完全查知工人的劳动量,只能通过观察产量(劳动量的信号)来推测。在劳动和产量分离的前提下再分析之前的几种激励方式
- Rent: 如果产量有随机分量,工人会承受风险——而工人实际上希望规避风险,于是这种incentive就是低效率的
- Wage labor: 如果所有者难以查知劳动投入量(而非小时数),这个就很难实施
- Take-it-or-leave-it: 同Wage labor。如果报酬取决于产量,那么工人承担全部风险
- Sharecropping: 工人和所有者共同承��担者产量波动的风险,工人有生产激励,而不必承担全部风险。
- 工人付出的劳动, 产量(设价格为1,这也成为价格的测度), 报酬, 劳动成本
提示
- 在第三类垄断的情况下,需要对 的大小进行分类讨论。
- asymptotically 渐近的/subsidizes 补助
- beneficial to produce
- 交换并且 实行一般垄断定价:计算出 可能的取值,而后令 利润最大 / 若 实行完全价格歧视,则保持 在无差异曲线上,且 的无差异曲线与之相切。
- 公共物品平衡的条件: ,